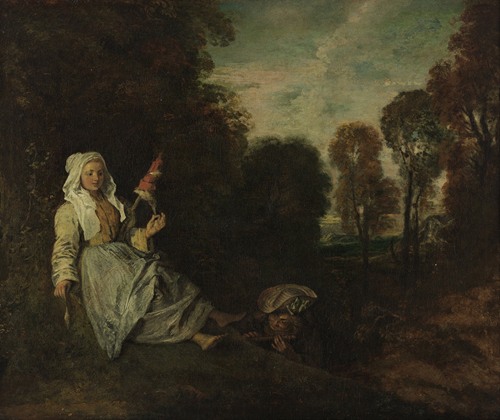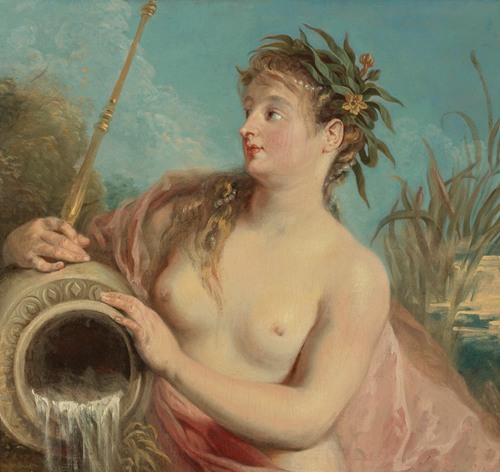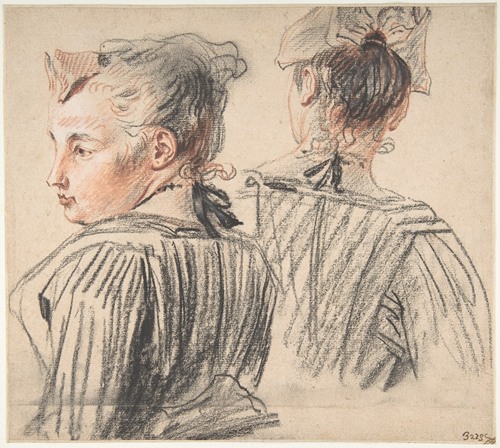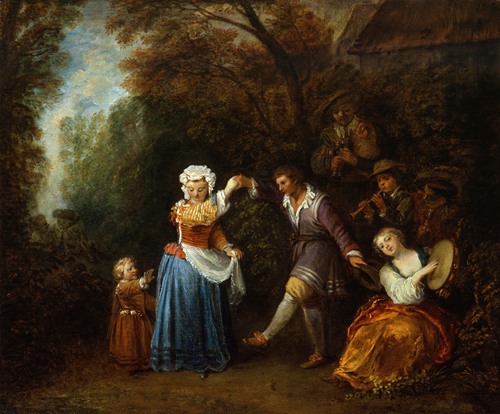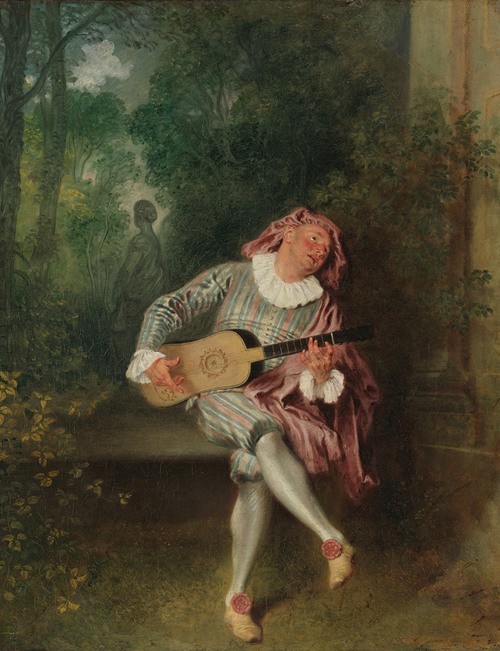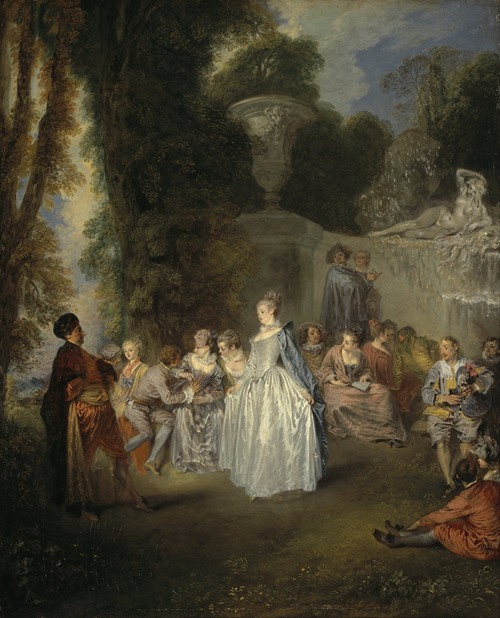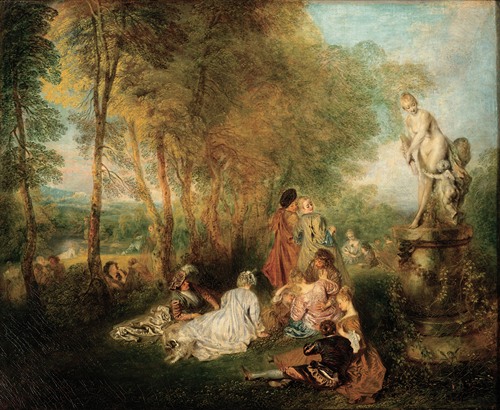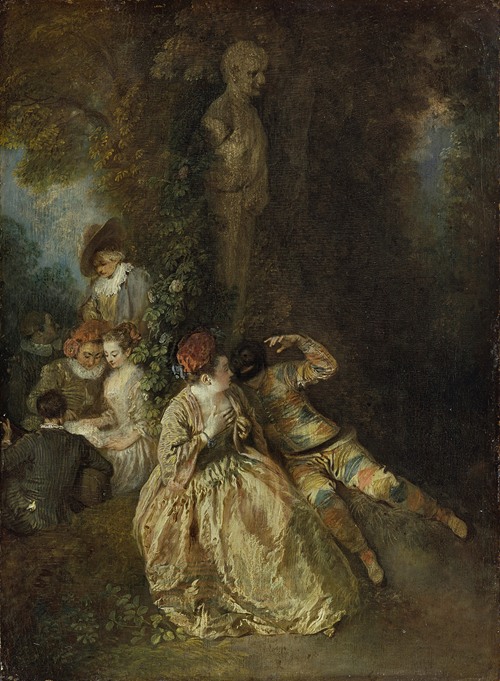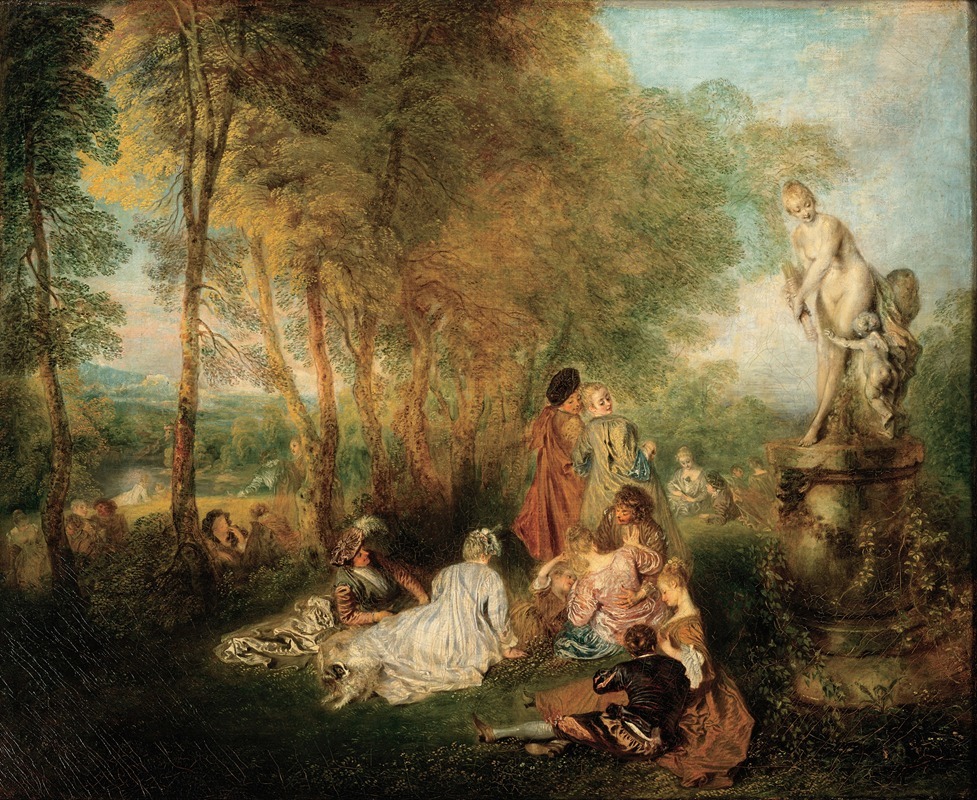

Jean-Antoine Watteau was a French painter and draughtsman whose brief career spurred the revival of interest in colour and movement, as seen in the tradition of Correggio and Rubens. He revitalized the waning Baroque style, shifting it to the less severe, more naturalistic, less formally classical, Rococo. Watteau is credited with inventing the genre of fêtes galantes, scenes of bucolic and idyllic charm, suffused with a theatrical air. Some of his best known subjects were drawn from the world of Italian comedy and ballet.
Jean-Antoine Watteau was born in October 1684 in Valenciennes, once an important town in the County of Hainaut which became sequently part of the Burgundian and Habsburg Netherlands until its secession to France following the Franco-Dutch War. He was the second of four sons born to Jean-Philippe Watteau (1660–1720) and Michelle Lardenois (1653–1727), and was presumed to be of Walloon descent. The Watteaus were a quite well-to-do family, although Jean-Philippe, a roofer in second generation, was said to be given to brawling. Showing an early interest in painting, Jean-Antoine may have been apprenticed to Jacques-Albert Gérin, a local painter, and his first artistic subjects were charlatans selling quack remedies on the streets of Valenciennes. Watteau left for Paris in 1702. After a period spent as a scene-painter, and in poor health, he found employment in a workshop at Pont Notre-Dame, making copies of popular genre paintings in the Flemish and Dutch tradition; it was in that period that he developed his characteristic sketchlike technique.
His drawings attracted the attention of the painter Claude Gillot, and by 1705 he was employed as an assistant to Gillot, whose work, influenced by those of Francesco Primaticcio and the school of Fontainebleau, represented a reaction against the turgid official art of Louis XIV's reign. In Gillot's studio Watteau became acquainted with the characters of the commedia dell'arte (which moved onto the théâtre de la foire following the Comédie-Italienne departure in 1697), a favorite subject of Gillot's that would become one of Watteau's lifelong passions.
After a quarrel with Gillot, Watteau moved to the workshop of Claude Audran III, an interior decorator, under whose influence he began to make drawings admired for their consummate elegance. Audran was the curator of the Palais du Luxembourg, and from him Watteau acquired his knowledge of decorative art and ornamental design. At the palace, Watteau was able to see the magnificent series of canvases painted by Peter Paul Rubens for Queen Marie de Medici. The Flemish painter would become one of his major influences, together with the Venetian masters that he would later study in the collection of his patron and friend, the banker Pierre Crozat.
During this period Watteau painted The Departing Regiment, the first picture in his second and more personal manner, showing influence of Rubens, and the first of a long series of camp pictures. He showed the painting to Audran, who made light of it, and advised him not to waste his time and gifts on such subjects. Watteau determined to leave him, advancing as excuse his desire to return to Valenciennes. He found a purchaser, at the modest price of 60 livres, in a man called Sirois, the father-in-law of his later friend and patron Edme-François Gersaint, and was thus enabled to return to the home of his childhood. In Valenciennes he painted a number of the small camp-pieces, notably the Camp-Fire, which was again bought by Sirois, the price this time being raised to 200 livres.
In 1709, Watteau tried to obtain a one-year stay in Rome by winning the Prix de Rome from the Academy, but managed only to get awarded with the second prize. In 1712 he tried again and was persuaded by Charles de La Fosse that he had nothing to learn from going to Rome; thanks to Fosse he was accepted as an associate member of the Academy in 1712 and a full member in 1717. He took those five years to deliver the required "reception piece", but it was one of his masterpieces: the Pilgrimage to Cythera, also called the Embarkation for Cythera.
Watteau then went to live with the collector Pierre Crozat, who eventually on his death in 1740 left around 400 paintings and 19,000 drawings by the masters. Thus Watteau was able to spend even more time becoming familiar with the works of Rubens and the Venetian masters. He lacked aristocratic patrons; his buyers were bourgeois such as bankers and dealers. Among his most famous paintings, beside the two versions of the Pilgrimage to Cythera, one in the Louvre, the other in the Schloss Charlottenburg, Berlin, are Pierrot (long identified as "Gilles"), Fêtes venitiennes, Love in the Italian Theater, Love in the French Theater, "Voulez-vous triompher des belles?" and Mezzetin. The subject of his hallmark painting, Pierrot (Gilles), is an actor in a white satin costume who stands isolated from his four companions, staring ahead with an enigmatic expression on his face.
Watteau's final masterpiece, the Shop-sign of Gersaint, exits the pastoral forest locale for a mundane urban set of encounters. Painted at Watteau's own insistence, "in eight days, working only in the mornings ... in order to warm up his fingers", this sign for the shop in Paris of the paintings dealer Edme François Gersaint is effectively the final curtain of Watteau's theatre. It has been compared with Las Meninas as a meditation on art and illusion. The scene is an art gallery where the façade has magically vanished, and the gallery and street in the canvas are fused into one contiguous drama.
Watteau alarmed his friends by a carelessness about his future and financial security, as if foreseeing he would not live for long. In fact he had been sickly and physically fragile since childhood. In 1720, he travelled to London, England, to consult Dr. Richard Mead, one of the most fashionable physicians of his time and an admirer of Watteau's work. However, London's damp and smoky air offset any benefits of Dr. Mead's wholesome food and medicines. Watteau returned to France, spending six months with Gersaint, and then spent his last few months on the estate of his patron, Abbé Haranger, where he died in 1721, perhaps from tuberculous laryngitis, at the age of 36. The Abbé said Watteau was semi-conscious and mute during his final days, clutching a paint brush and painting imaginary paintings in the air.
His nephew, Louis Joseph Watteau, son of Antoine's brother Noël Joseph Watteau (1689–1756), and grand nephew, François-Louis-Joseph Watteau, son of Louis, followed Antoine into painting.