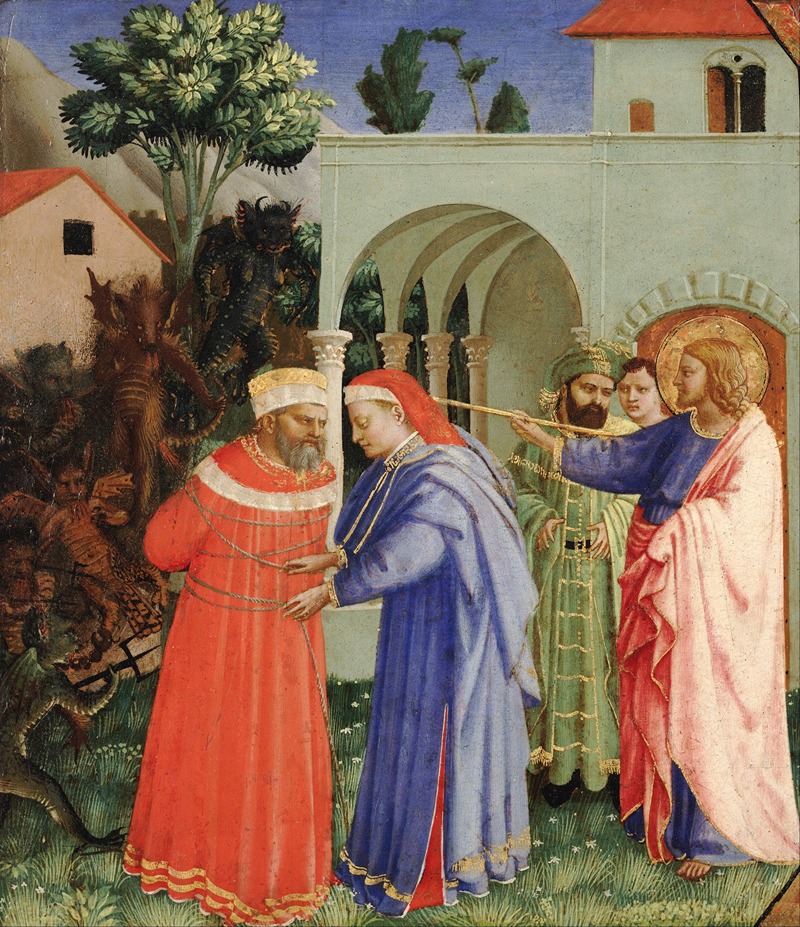
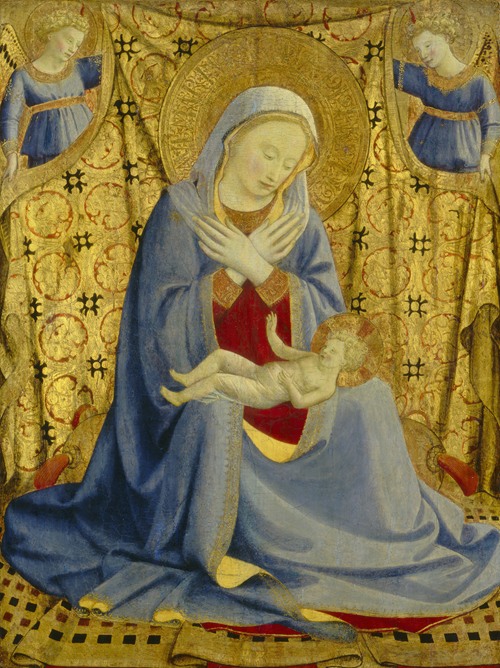
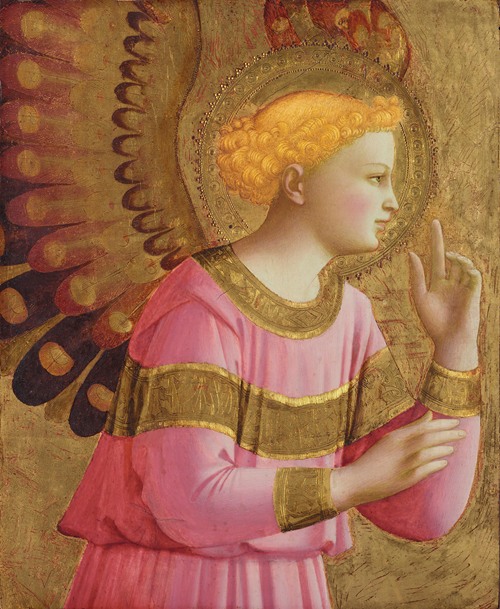
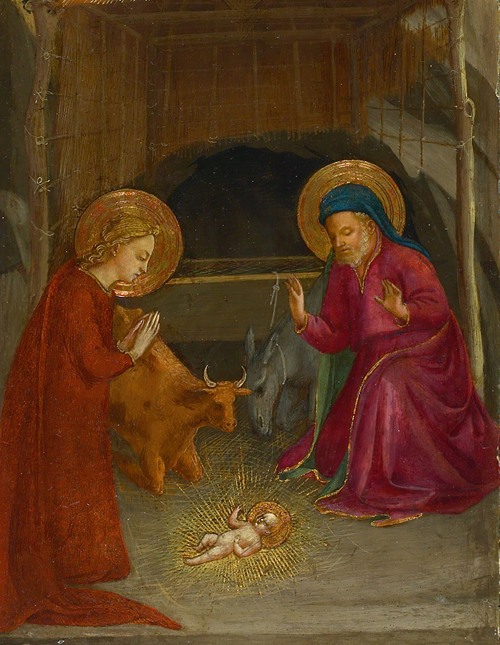
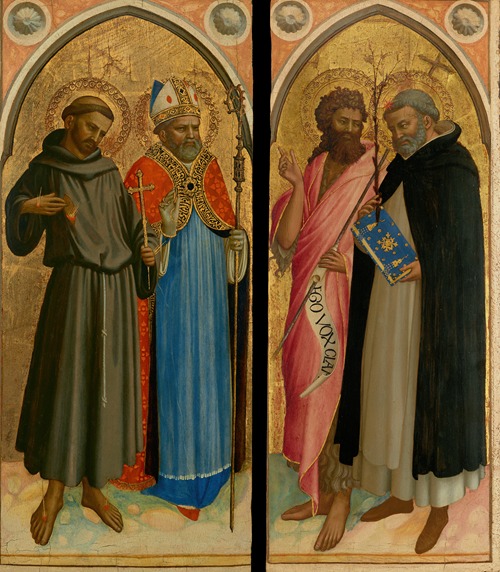
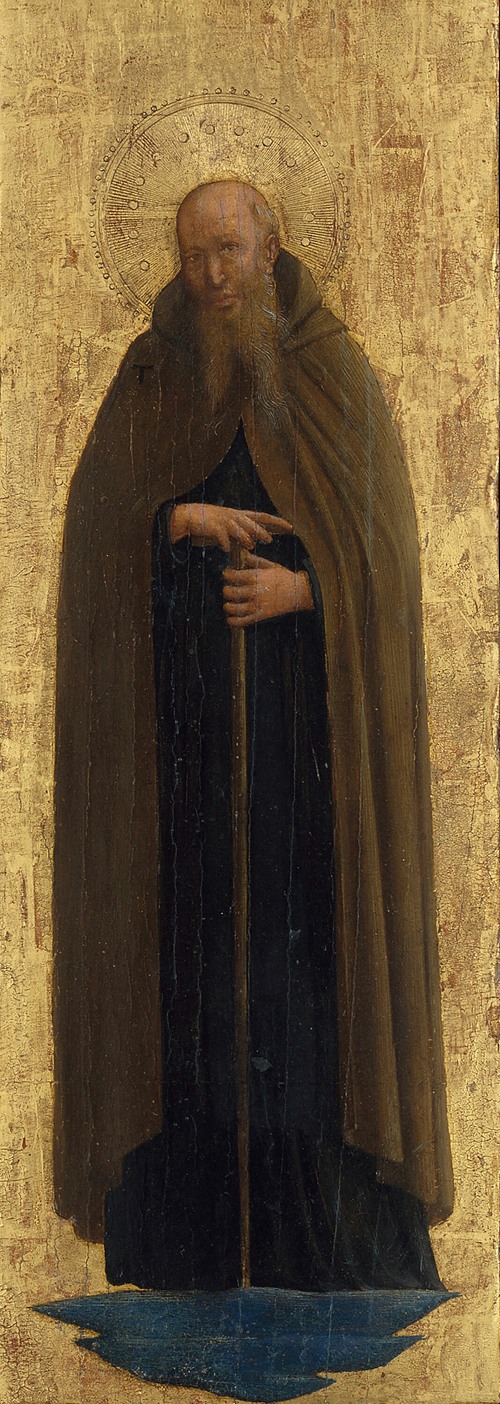
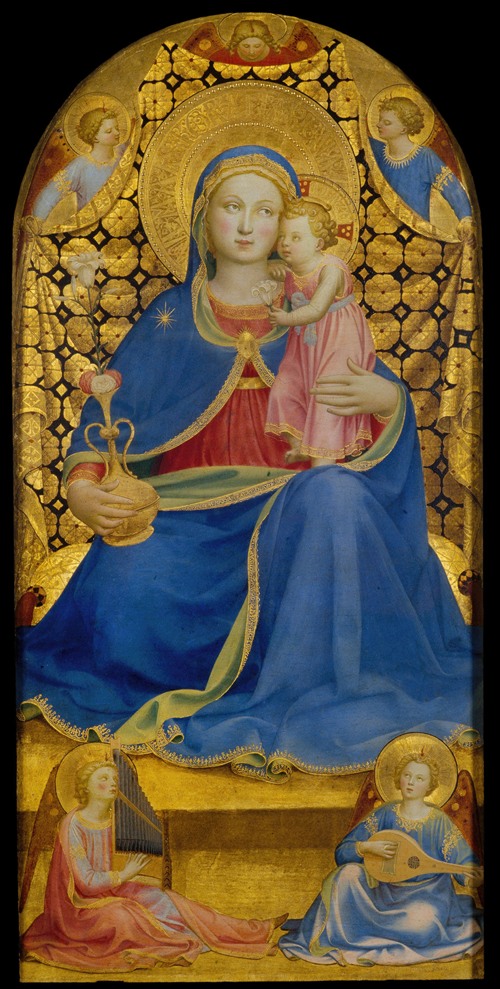
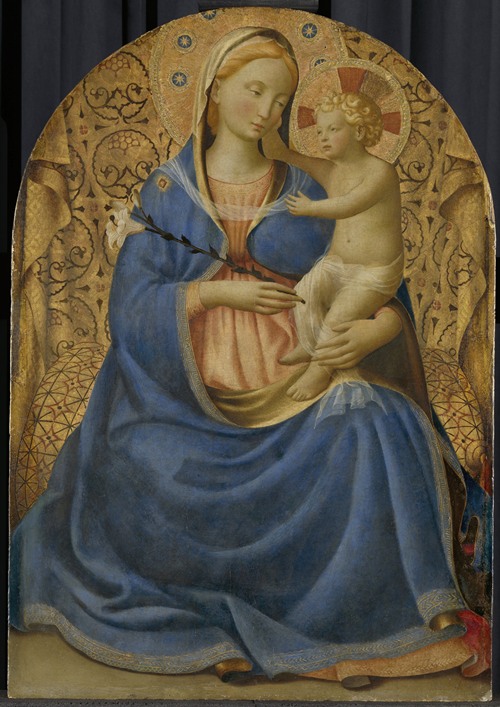
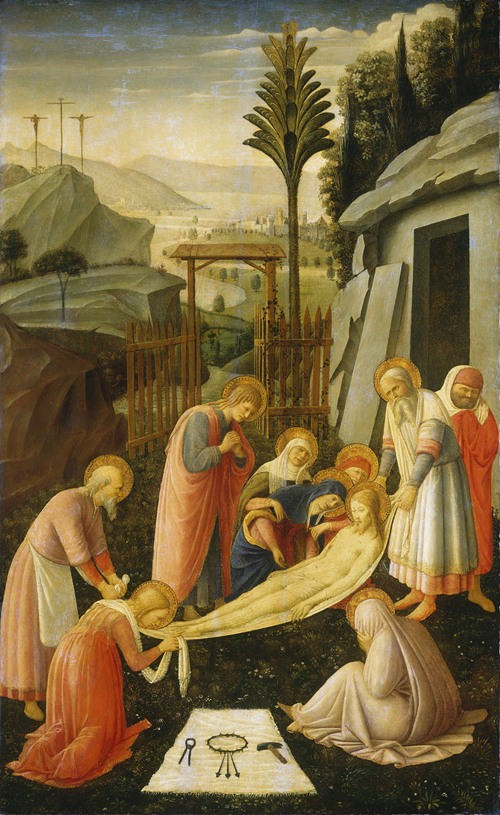
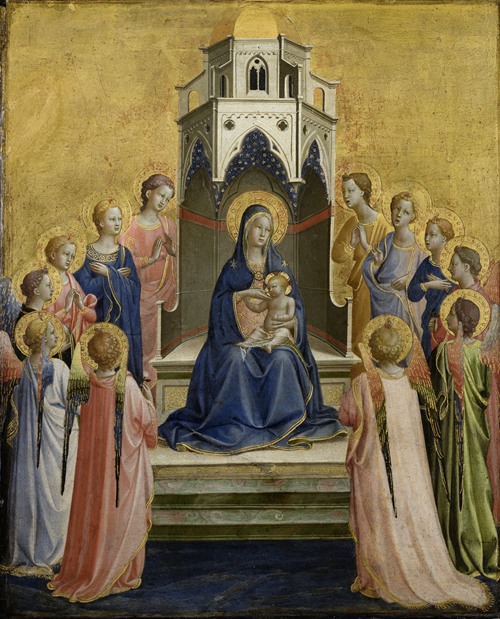
Fra Angelico (born Guido di Pietro) was an Italian painter of the Early Renaissance, described by Vasari in his Lives of the Artists as having "a rare and perfect talent". He earned his reputation primarily for the series of frescoes he made for his own friary, San Marco, in Florence.
He was known to contemporaries as Fra Giovanni da Fiesole (Brother John of Fiesole) and Fra Giovanni Angelico (Angelic Brother John). In modern Italian he is called Beato Angelico (Blessed Angelic One); the common English name Fra Angelico means the "Angelic friar".
In 1982, Pope John Paul II proclaimed his beatification in recognition of the holiness of his life, thereby making the title of "Blessed" official. Fiesole is sometimes misinterpreted as being part of his formal name, but it was merely the name of the town where he took his vows as a Dominican friar, and was used by contemporaries to separate him from others who were also known as Fra Giovanni. He is listed in the Roman Martyrology as Beatus Ioannes Faesulanus, cognomento Angelicus—"Blessed Giovanni of Fiesole, surnamed 'the Angelic' ".
Fra Angelico was born Guido di Pietro at Rupecanina in the Tuscan area of Mugello near Fiesole towards the end of the 14th century. Nothing is known of his parents. He was baptized Guido or Guidolino. The earliest recorded document concerning Fra Angelico dates from October 17, 1417 when he joined a religious confraternity or guild at the Carmine Church, still under the name of Guido di Pietro. This record reveals that he was already a painter, a fact that is subsequently confirmed by two records of payment to Guido di Pietro in January and February 1418 for work done in the church of Santo Stefano del Ponte. The first record of Angelico as a friar dates from 1423, when he is first referred to as Fra Giovanni (Friar John), following the custom of those entering one of the older religious orders of taking a new name. He was a member of the local community at Fiesole, not far from Florence, of the Dominican Order; one of the medieval Orders belonging to a category known as mendicant Orders because they generally lived not from the income of estates but from begging or donations. Fra, a contraction of frater (Latin for 'brother'), is a conventional title for a mendicant friar.
According to Vasari, Fra Angelico initially received training as an illuminator, possibly working with his older brother Benedetto who was also a Dominican and an illuminator. The former Dominican convent of San Marco in Florence, now a state museum, holds several manuscripts that are thought to be entirely or partly by his hand. The painter Lorenzo Monaco may have contributed to his art training, and the influence of the Sienese school is discernible in his work. He also trained with master Varricho in Milan He had several important charges in the convents he lived in, but this did not limit his art, which very soon became famous. According to Vasari, the first paintings of this artist were an altarpiece and a painted screen for the Charterhouse (Carthusian monastery) of Florence; none such exist there now.
From 1408 to 1418, Fra Angelico was at the Dominican friary of Cortona, where he painted frescoes, now mostly destroyed, in the Dominican Church and may have been assistant to Gherardo Starnina or a follower of his. Between 1418 and 1436 he was at the convent of Fiesole, where he also executed a number of frescoes for the church and the Altarpiece, which was deteriorated but has since been restored. A predella of the Altarpiece remains intact and is conserved in the National Gallery, London, and is a great example of Fra Angelico's ability. It shows Christ in Glory surrounded by more than 250 figures, including beatified Dominicans. In this period he painted some of his masterpieces including a version of The Madonna of Humility, well preserved and property of the Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum but on loan to the MNAC of Barcelona, an Annunciation along with a Madonna of the Pomegranate, at the Prado Museum.
In 1436, Fra Angelico was one of a number of the friars from Fiesole who moved to the newly built convent or friary of San Marco in Florence. This was an important move which put him in the centre of artistic activity of the region and brought about the patronage of Cosimo de' Medici, one of the wealthiest and most powerful members of the city's governing authority (or "Signoria") and founder of the dynasty that would dominate Florentine politics for much of the Renaissance. Cosimo had a cell reserved for himself at the friary in order that he might retreat from the world. It was, according to Vasari, at Cosimo's urging that Fra Angelico set about the task of decorating the convent, including the magnificent fresco of the Chapter House, the often-reproduced Annunciation at the top of the stairs leading to the cells, the Maesta (or Coronation of the Madonna) with Saints (cell 9) and the many other devotional frescoes, of smaller format but remarkable luminous quality, depicting aspects of the Life of Christ that adorn the walls of each cell.
In 1439 Fra Angelico completed one of his most famous works, the San Marco Altarpiece at Florence. The result was unusual for its time. Images of the enthroned Madonna and Child surrounded by saints were common, but they usually depicted a setting that was clearly heaven-like, in which saints and angels hovered about as divine presences rather than people. But in this instance, the saints stand squarely within the space, grouped in a natural way as if they were able to converse about the shared experience of witnessing the Virgin in glory. Paintings such as this, known as Sacred Conversations, were to become the major commissions of Giovanni Bellini, Perugino and Raphael.
In 1445 Pope Eugene IV summoned him to Rome to paint the frescoes of the Chapel of the Holy Sacrament at St Peter's, later demolished by Pope Paul III. Vasari claims that at this time Fra Angelico was offered the Archbishopric of Florence by Pope Nicholas V, and that he refused it, recommending another friar for the position. The story seems possible and even likely. However, if Vasari's date is correct, then the pope must have been Eugene IV and not Nicholas, who was elected Pope only on 6 March 1447. Moreover, the archbishop in 1446–1459 was the Dominican Antoninus of Florence (Antonio Pierozzi), canonized by Pope Adrian VI in 1523. In 1447 Fra Angelico was in Orvieto with his pupil, Benozzo Gozzoli, executing works for the Cathedral. Among his other pupils were Zanobi Strozzi.
From 1447 to 1449 Fra Angelico was back at the Vatican, designing the frescoes for the Niccoline Chapel for Nicholas V. The scenes from the lives of the two martyred deacons of the Early Christian Church, St. Stephen and St. Lawrence may have been executed wholly or in part by assistants. The small chapel, with its brightly frescoed walls and gold leaf decorations gives the impression of a jewel box. From 1449 until 1452, Fra Angelico returned to his old convent of Fiesole, where he was the Prior.
In 1455, Fra Angelico died while staying at a Dominican convent in Rome, perhaps on an order to work on Pope Nicholas' chapel. He was buried in the church of Santa Maria sopra Minerva.