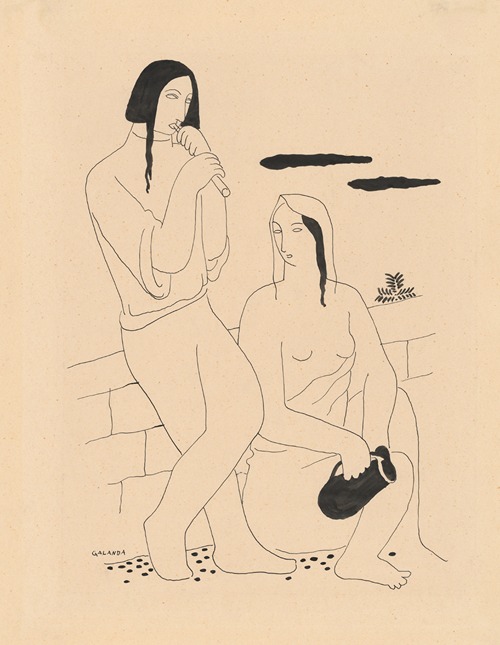

Mikuláš Galanda was a painter and illustrator who was one of the most important pioneers and propagators of Slovak modern art. He is buried in the National Cemetery in Martin.
He was born in Mala Vieska near Turčianske Teplice. From 1914 to 1916 he studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Budapest. In 1922 he enrolled in the Academy of Arts, Architecture and Design in Prague, where he studied under Prof. V. H. Brunner. From 1923 to 1927 he studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Prague under August Brömse and Franz Thiele.
From 1924 to 1926, Galanda was the first graphical editor for Dav magazine. He was given approval to teach drawing in 1928, and in that year in Prague he met Maria Boudova, whom he married in 1931. He moved to Bratislava in 1929 and started to teach at 1st girls' town school.
From 1929 to 1932 he shared an atelier together with Ľudovít Fulla situated in 5, Trnavska street in Bratislava. In 1930 he worked as a teacher at 2nd boys' school and at School of handcrafts in Bratislava. He joined Umelecka beseda slovenska. In autumn of 1930 he traveled to Paris, and had an exhibition in Kraków.
During 1930–1932, Galana and L. Fulla released four issues of their Private Letters, in which they had been talking over new progressive opinions in fine arts and its function in modern society. In 1933 he became a professor at School of handcrafts in Bratislava, and won Krajinska cena M. R. Štefánika.
In 1935 he had exhibitions in Siena Elanu and Prague. In 1936 he had a holiday in Zdiar, and exhibited in the Venice Biennale. In 1937 he exhibited his works in Moscow and at the 1937 Exposition Internationale des Arts et Techniques dans la Vie Moderne in Paris, where he won a Silver Medal for inventive art genre – illustrations and book designs.
In 1938 he participated in an Exhibition of Slovak Art in New York. He signed the manifesto of 300 cultural, artistic, scientific and religious representatives "Verní zostaneme! (Forever faithful!)" in protest against ČSR separation.
Mikuláš Galanda died on 5 June 1938 in Bratislava.
In all his work, he strove to formulate the Slovakian artistic modernism on the basis of achievements in the development of European painting. He was inclined towards expressionist and cubist trends, and created his own form of painting on this basis. Early in his career he was oriented toward graphics but later he devoted himself more to painting. His subject matter was domestic, associated with the Slovak landscape and people. He was considered to be a lyric painter of female beauty and charm. His body of work is predominantly melancholic in tone.
More Artworks by Mikuláš Galanda (View all 609 Artworks)