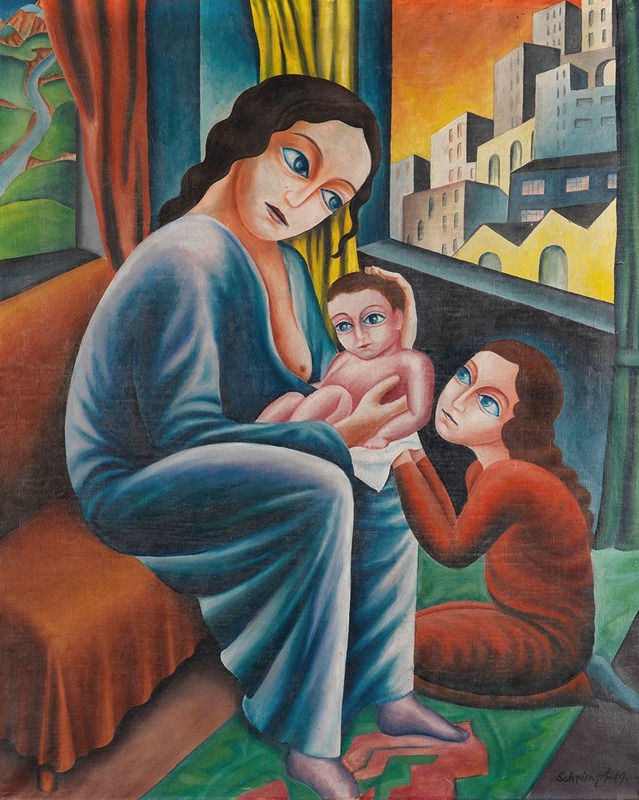
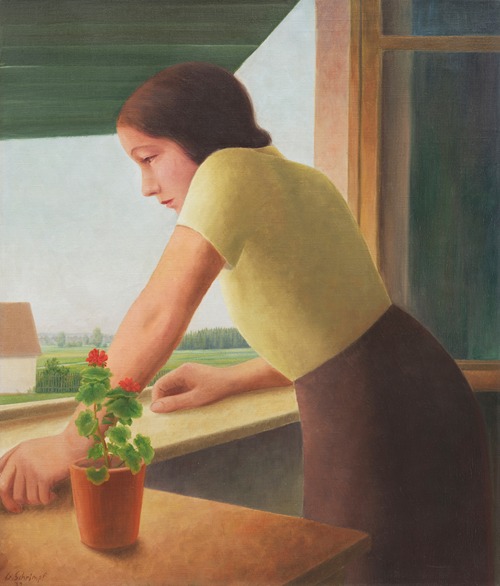
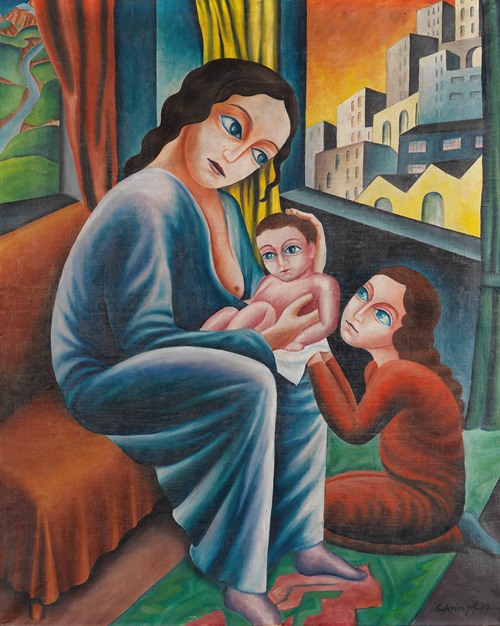
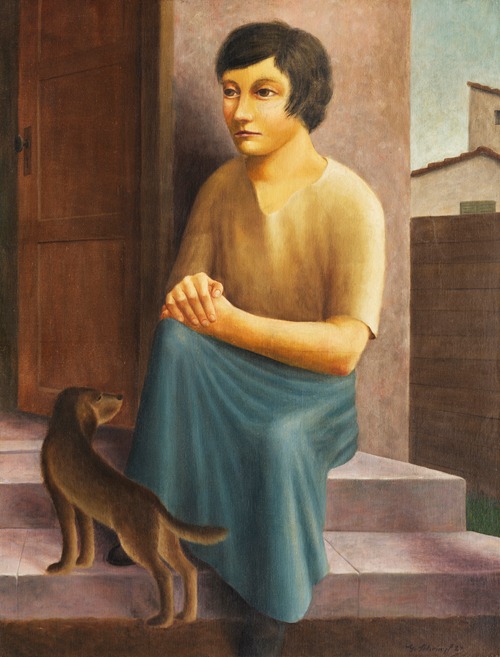
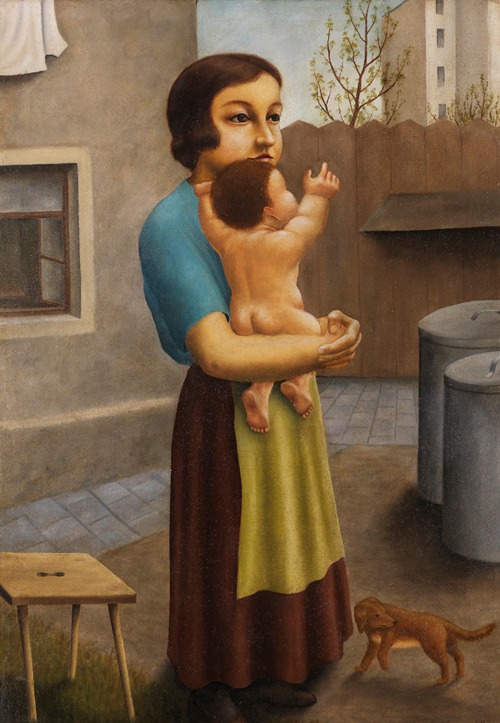
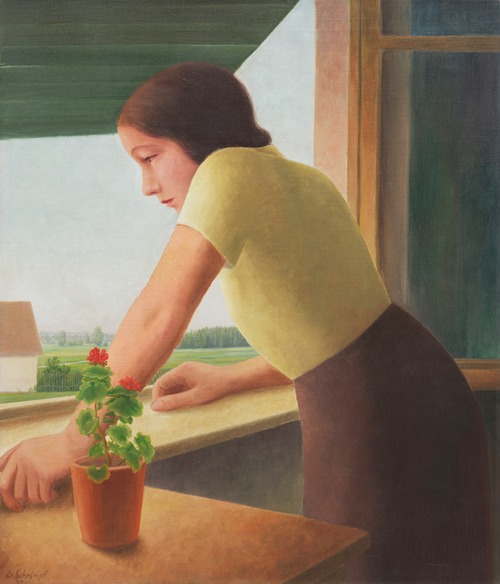
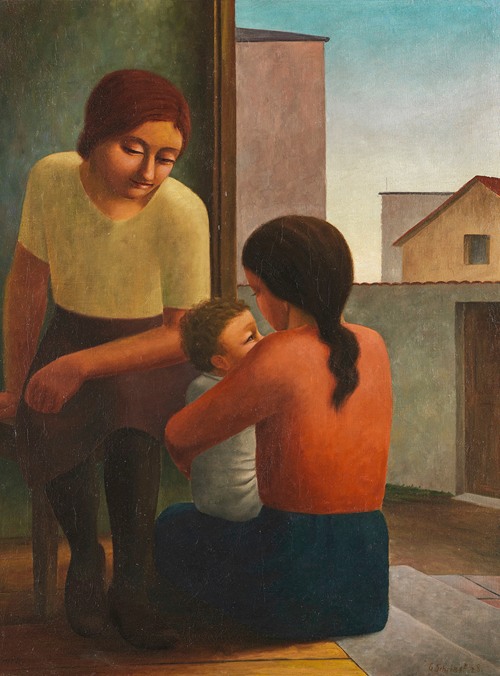
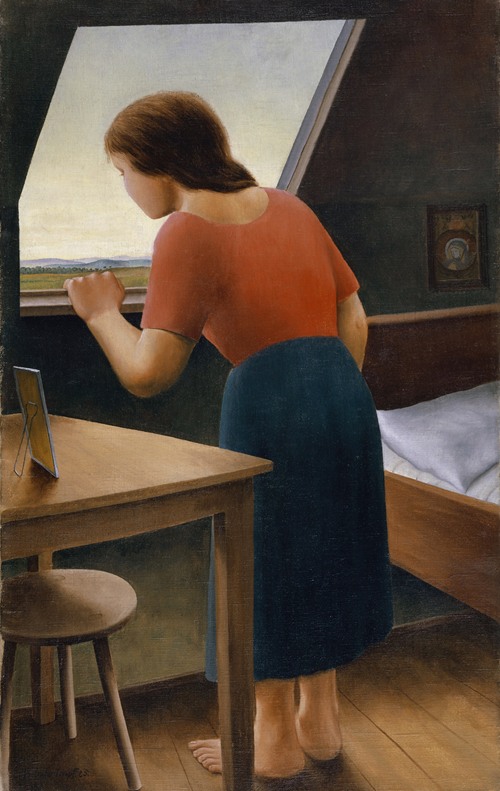
Georg Schrimpf was a German painter and graphic artist. Along with Otto Dix, George Grosz and Christian Schad, Schrimpf is broadly acknowledged as a main representative of the art movement Neue Sachlichkeit (usually translated New Objectivity), which developed, in Weimar Germany, from 1919 to 1933, as an outgrowth of Expressionism. Schrimpf was listed as a producer of Degenerate Art by the German National Socialist government in the 1930s.
Schrimpf was born in Munich, his father having died before Schrimpf's birth. His stepfather later forced him to leave home. In 1902 he apprenticed as a baker in Passau. From 1905 to 1914 Schrimpf wandered through Belgium, France, Switzerland and Northern Italy, working as a waiter, baker, and coal shuffler. In 1913 he lived in an anarchist colony in Switzerland, where he formed a friendship with Oskar Maria Graf, also a baker, but later a famous novelist.
With the outbreak of the First World War, the antimilitaristic Schrimpf "successfully employed every possible trick to avoid military service; in so doing, however, he ruined his health". From 1915–1918 Schrimpf lived in Berlin, where he worked as a freelance artist. In his free time he used every minute for drawing, painting, and wood carving. Mostly self-taught as an artist, he learned by copying the Old Masters.
In 1916 the famous publicist and art expert Herwarth Walden exhibited some of Schrimpf's paintings and woodcarvings in his Berlin gallery Der Stumm where they received much public attention. At this time and in this gallery Schrimpf met the painter Maria Uhden. The two married in 1917 but she died the following year, due to complications from the birth of their son Mark. He participated with the November Group and was included in their exhibitions of 1919, 1920, 1924 and 1929. Schrimpf published works, in such the Munich expressionist magazines as Der Weg, Die Bücherkiste and Die Sichel. In 1919 he was involved in the short-lived Munich Soviet Republic which attempted to establish a socialist state in Bavaria and was arrested after the movement was crushed. In 1921 his works were shown in Munich by art dealer Hans Goltz.
As early as the 1920s, Schrimpf was regarded as being a representative of the "right wing" of the Neue Sachlichkeit movement. Other prominent representatives of the wing included Alexander Kanoldt and Franz Lenk. The movement's so called "verist" wing included such artists as Otto Dix, George Grosz and Georg Scholz. In 1924 he moved to Italy where his second wife, Hedwig Marshall, found work as a nurse.
In 1925 Schrimpf participated in the Neue Sachlichkeit exhibition at the Mannheim Kunsthalle. Two years later, he began teaching at the Meisterschule für Dekorationskunst in Munich. The "right-wing" of the movement were not immediately condemned by the Nazi regime at an early stage and were able to take on professorships in painting after the regime seized power in 1933. Schrimpf's work was seen as an acceptable form of German Romanticism by the authorities.
1932 saw the foundation of the Group Seven and the start of a touring exhibition by the group; the other members were Theo Champion, Adolf Dietrich, Hasso von Hugo, Franz Radziwill, as well as Kanoldt and Lenk.
Schrimpf became professor at the Royal School of Art in Berlin in 1933, but was fired in 1937 because of his “red past”. He had been a short-time member of Rote Hilfe, a socialist organization. For the same reason the Nazi regime banned his works from public exhibitions. Schrimpf died in Berlin on 19 April 1938.