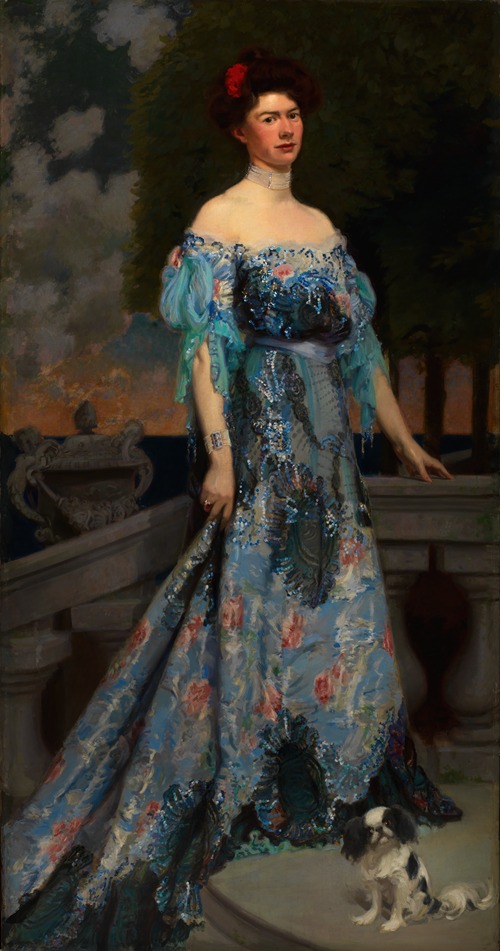
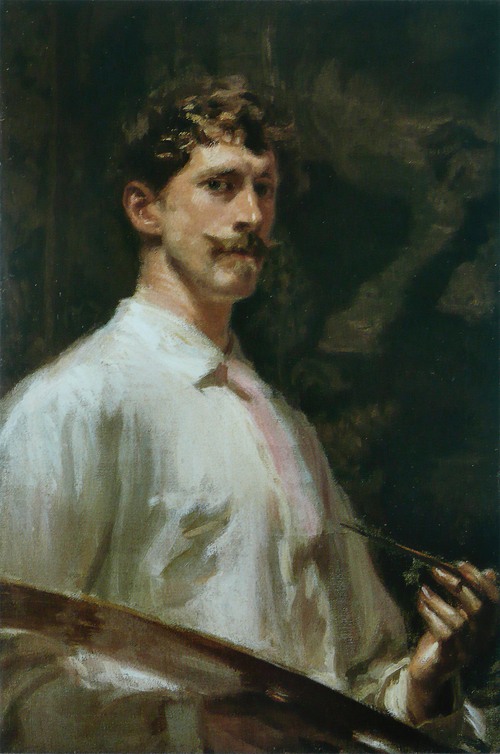
Frederick William MacMonnies was the best known expatriate American sculptor of the Beaux-Arts school, as successful and lauded in France as he was in the United States. He was also a highly accomplished painter and portraitist. He was born in Brooklyn Heights, Brooklyn, New York and died in New York City.
Three of MacMonnies' best-known sculptures are Nathan Hale, Bacchante and Infant Faun, and Diana.
In 1880 MacMonnies began an apprenticeship under Augustus Saint-Gaudens, and was soon promoted to studio assistant, beginning his lifelong friendship with the acclaimed sculptor. MacMonnies studied at night with the National Academy of Design and The Art Students League of New York. In Saint-Gaudens' studio, he met Stanford White, who was turning to Saint-Gaudens for the prominent sculptures required for his architecture.
In 1884 MacMonnies traveled to Paris to study sculpture at the École des Beaux-Arts, twice winning the highest award given to foreign students. In 1888 he opened a studio in Paris and began to create some of his most famous sculptures, which he submitted annually to the Paris Salon. In his atelier, he mentored such notable artists as Janet Scudder and Mary Foote. He was taught at the Académie Vitti in 1904.
The life-size Nathan Hale was the first major commission gained by MacMonnies. Erected in 1890 in City Hall Park, New York, it stands near where the actual Nathan Hale was thought to have been executed. Copies are scattered in museums across the United States, since MacMonnies was one of the earliest American sculptors to supplement his fees from major commissions by selling reduced-size reproductions to the public. The Metropolitan Museum has a copy, as do the Art Museum at Princeton University, the National Gallery of Art, Phoenix Art Museum, Orlando Museum of Art, and the Mead Art Museum at Amherst College.
In 1888, the intervention of Stanford White gained MacMonnies two major commissions for garden sculpture for influential Americans, a decorative Pan fountain sculpture for Rohallion, the New Jersey mansion of banker Edward Adams, who opened for him a social circle of art-appreciating New Yorkers, and a work for ambassador Joseph H. Choate, at Naumkeag, in Stockbridge, Massachusetts.
In 1889 an Honorable Mention at the Paris Salon for his Diana led to further and more public American commissions, including spandrel reliefs for Stanford White's permanent Washington Arch, New York, and the Nathan Hale memorial in City Hall Park, dedicated in 1893. Until the outbreak of World War I, when he gave up his grand household establishment in Paris, MacMonnies travelled annually to the United States to see dealers and patrons, returning to Paris to work on his commissions. His long-term residence was at Giverny.
In 1891, he designed the statue of James S. T. Stranahan in Brooklyn. That same year, he was awarded the commission for the Columbian Fountain, the centerpiece of the 1893 World's Columbian Exposition in Chicago: the sculpture of Columbia in her Grand Barge of State, in the vast central fountain of the Court of Honor, was truly the iconic figure at the heart of the American Beaux-Arts movement. This large decorative fountain piece became the focal point at the Exposition and established MacMonnies as one of the important sculptors of the time.
In 1894, Stanford White brought another prestigious and highly visible commission, for three bronze groups for the Soldiers and Sailors Memorial Arch in Brooklyn's Grand Army Plaza. The complicated figural groups occupied him for the next eight years.(Bogart, p. 35)
Around the turn of the century, MacMonnies was commissioned to design the equestrian statue of Henry Warner Slocum in Brooklyn, which was dedicated in 1905.
Due to fame gathered from the 1893 World's Columbian Exposition, he was commissioned to produce a large public sculpture celebrating the pioneers of the American Old West, his only work on this subject. MacMonnies began the work in 1906, and the work was unveiled in 1911. The monument features a depiction of Kit Carson, and it marks the end of the Smoky Hill Trail, a popular route to Colorado Territory taken by gold-seekers, located near the Smoky Hill River. Meanwhile he was still creating portraits and his 1904 full length painting of his student Mabel Conkling was said to be his "finest .. yet".
Commissioned in 1908, his Princeton Battle Monument, created in collaboration with architects Carrere & Hastings, located in Princeton, New Jersey was not completed until 1922.(Clark 1984)
Returning to New York after 1915, he continued his stylish work with the colossal group, Civic Virtue, a fountain for New York City Hall (1909–22). It was the subject of considerable controversy because it depicts a man trampling several female figures, representing evil sirens. This resulted in considerable public criticism. The statue was moved in 1941 to distant Queens Borough Hall and subsequently in December 2013 to Green-Wood Cemetery in Brooklyn.
In late 1917, MacMonnies was commissioned by a group of influential citizens of New York City, to work on a sculpture in honor of those who died in the First Battle of the Marne, as a gift to the French people in exchange for the Statue of Liberty. Called, in French, La Liberté éplorée ("The Tearful Liberty") the statue, located in Meaux, France, is over seven stories tall, at 22 metres (72 ft). The architect was American neo-classicist Thomas Hastings. While work started on the statue in 1924, it was not finished until 1932. At the time of its dedication, it was the world's largest stone monument. In 2011, the Musée de la Grande Guerre du pays de Meaux opened next to the monument.
The World War I Memorial, in Atlantic City, New Jersey, houses a 9-foot (2.7 m) bronze version of the statue.
Selected to sculpt the fourth issue of the long running Society of Medalists in 1931, MacMonnies chose to celebrate Charles Lindbergh's solo Trans-Atlantic flight of 1927. The powerful bust of Lindbergh on the obverse, combined with the reverse's dramatic allegorical depiction of a lone eagle battling across the sea, mark this issue as one of the more popular of the series.
Frederick William MacMonnies died of pneumonia in 1937, aged 73.