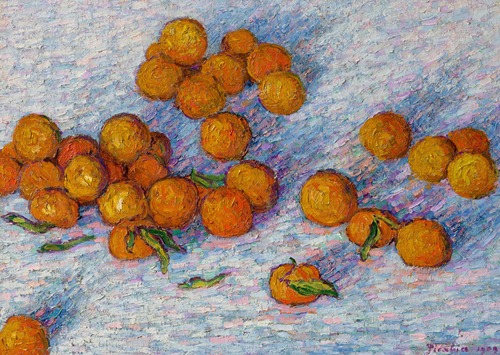Francis Picabia was a French avant-garde painter, poet and typographist. After experimenting with Impressionism and Pointillism, Picabia became associated with Cubism. His highly abstract planar compositions were colourful and rich in contrasts. He was one of the early major figures of the Dada movement in the United States and in France. He was later briefly associated with Surrealism, but would soon turn his back on the art establishment.
Francis Picabia was born in Paris of a French mother and a Cuban father of Spanish descent. Some sources would have his father as of aristocratic Spanish descent, whereas others consider him of non-aristocratic Spanish descent, from the region of Galicia. His birth year of 1879 coincided with the Spanish-Cuban Little War; and though Picabia was born in Paris, his father was involved in Cuban-French relations and would later serve as attaché at the Cuban legation in Paris (see the Treaty of 1898). The family ties to Cuba would be important in Picabia's life later on.
The family was affluent, but not without tragedy. Picabia's mother died of tuberculosis when he was seven and her mother died soon after. He was raised by his father.
Picabia's artistic ability was apparent from his youth. In 1894, he copied a collection of Spanish paintings that belonged to his grandfather, switching the copies for the originals and selling the originals to finance his stamp collection.
During the late 1890s, Picabia began to study art under Fernand Cormon and others at École des Arts Decoratifs, Cormon's academy at 104 boulevard de Clichy, where Van Gogh and Toulouse-Lautrec had also studied. From the age of twenty Picabia lived by painting. Subsequently, he inherited money from his mother, making him financially independent.
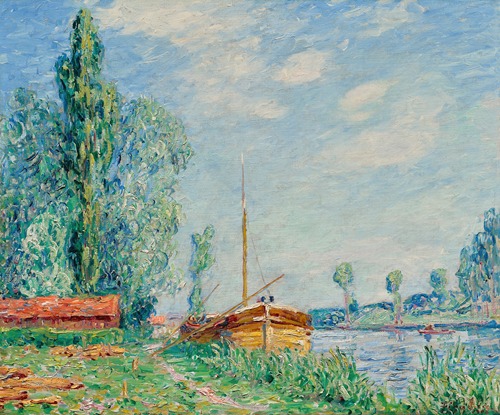
Early in his career, from 1903 to 1908, Picabia was influenced by the Impressionist paintings of Alfred Sisley. His subject matter included small churches, lanes, roofs of Paris, riverbanks, wash houses, and barges. This led critics to question his originality, saying that he copied Sisley, that his cathedrals looked like Monet cathedrals, or that he painted like Signac.
From 1909, his style changed as he came under the influence of a group of artists soon to be called Cubists. These artists would later form the Golden Section (Section d'Or). The same year, Picabia married Gabrielle Buffet.
Around 1911 Picabia joined the Puteaux Group, whose members he had met at the studio of Jacques Villon in Puteaux, a commune in the western suburbs of Paris. There he became friends with artist Marcel Duchamp and close friends with Guillaume Apollinaire. Other group members included Albert Gleizes, Roger de La Fresnaye, Fernand Léger and Jean Metzinger.
From 1913 to 1915 Picabia traveled to New York City several times and took an active part in the avant-garde movements, introducing Modern art to America. During that same era, France became embroiled in war. In 1915 Picabia again traveled to the United States en route to Cuba to buy molasses for a friend of his—the director of a sugar refinery. He landed in New York in June 1915. Though the stopover was ostensibly meant to be a simple port of call, he became intrigued with the city and his stay became prolonged.
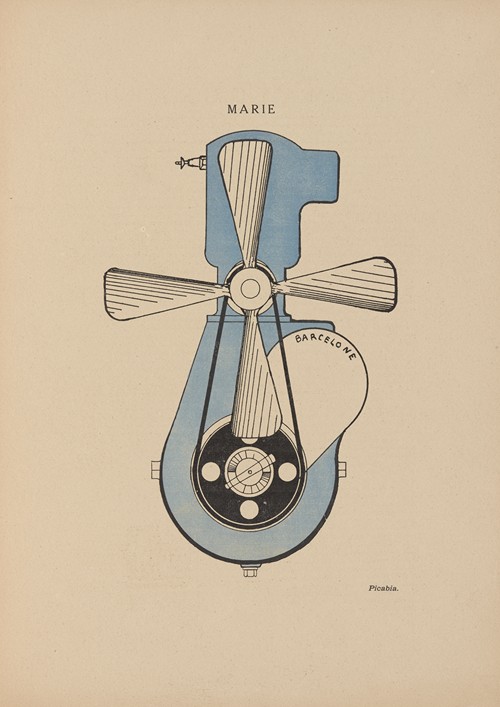
The magazine 291 devoted an entire issue to him, he met Man Ray, Gabrielle and Duchamp joined him, drugs and alcohol became a problem and his health declined. He suffered from dropsy and tachycardia. These years can be characterized as Picabia's proto-Dada period, consisting mainly of his portraits mécaniques.
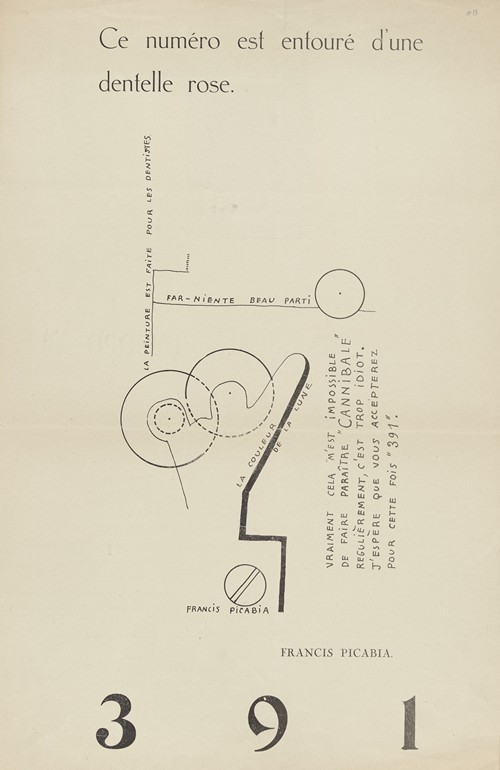
Later, in 1916, while in Barcelona and within a small circle of refugee artists that included Albert Gleizes and his wife Juliette Roche, Marie Laurencin, Olga Sacharoff, Robert Delaunay and Sonia Delaunay, he started his Dada periodical 391 (published by Galeries Dalmau), modeled on Stieglitz's own periodical. He continued the periodical with the help of Marcel Duchamp in the United States. In Zurich, seeking treatment for depression and suicidal impulses, he had met Tristan Tzara, whose radical ideas thrilled Picabia. Back in Paris, and now with his mistress Germaine Everling, he was in the city of "les assises dada" where André Breton, Paul Éluard, Philippe Soupault and Louis Aragon met at Certa, a Basque bar in the Passage de l'Opera. Picabia, the provocateur, was back home.
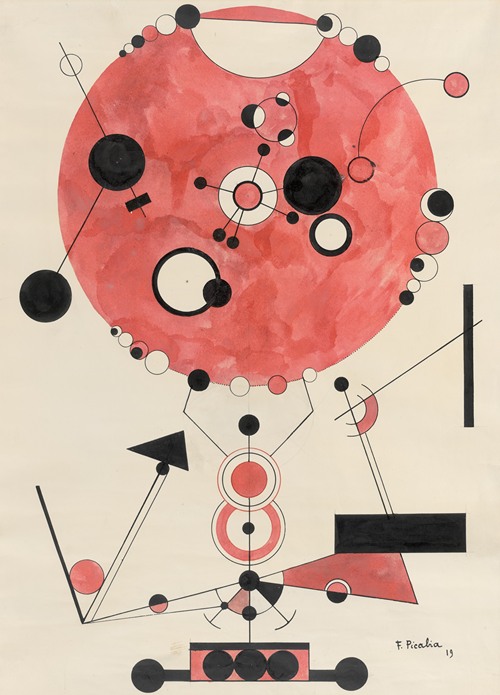
Picabia continued his involvement in the Dada movement through 1919 in Zürich and Paris, before breaking away from it after developing an interest in Surrealist art. (See Cannibale, 1921.) He denounced Dada in 1921, and issued a personal attack against Breton in the final issue of 391, in 1924.
The same year, he put in an appearance in the René Clair surrealist film Entr'acte, firing a cannon from a rooftop. The film served as an intermission piece for Picabia's avant-garde ballet, Relâche, premiered at the Théâtre des Champs-Élysées, with music by Erik Satie.
In 1922, André Breton relaunched Littérature magazine with cover images by Picabia, to whom he gave carte blanche for each issue. Picabia drew on religious imagery, erotic iconography, and the iconography of games of chance.
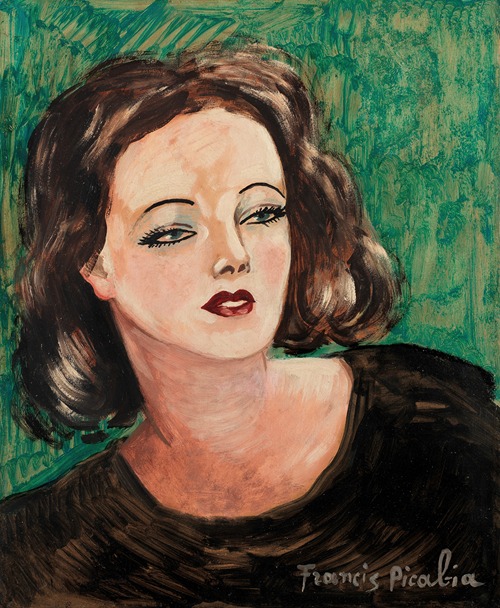
In 1925, Picabia returned to figurative painting, and during the 1930s became a close friend of the modernist novelist Gertrude Stein. In the early 1940s he moved to the South of France, where his work took a surprising turn: he produced a series of paintings based on the nude glamour photos in French "girlie" magazines like Paris Sex-Appeal, in a garish style which appears to subvert traditional, academic nude painting. Some of these went to an Algerian merchant who sold them, and so it passed that Picabia came to decorate brothels across North Africa under the Occupation.
Before the end of World War II, he returned to Paris where he resumed abstract painting and writing poetry. A large retrospective of his work was held at the Galerie René Drouin in Paris in the spring of 1949. Francis Picabia died in Paris in 1953 and was interred in the Cimetière de Montmartre.