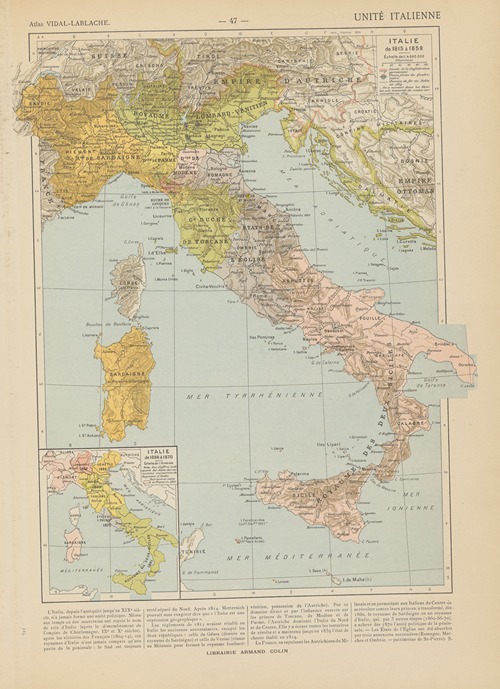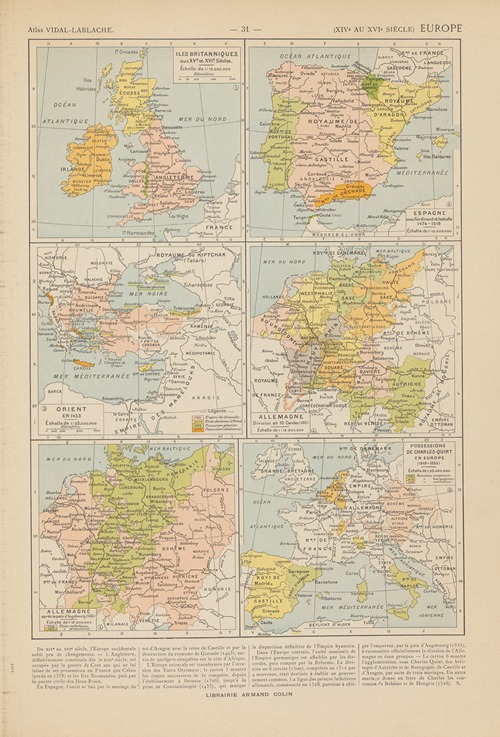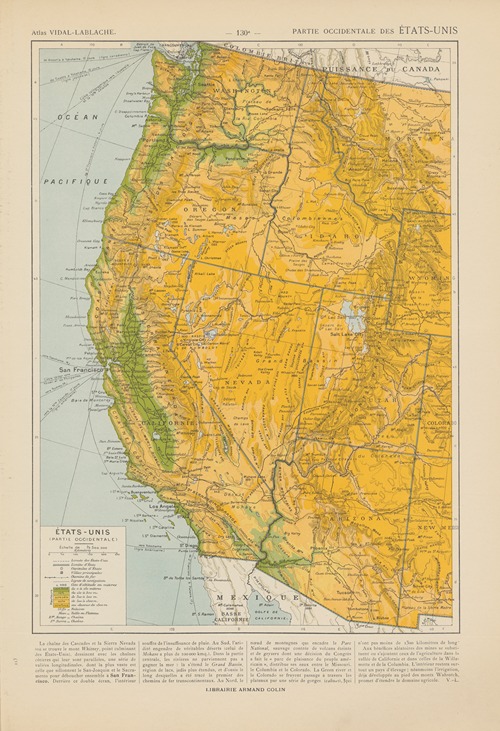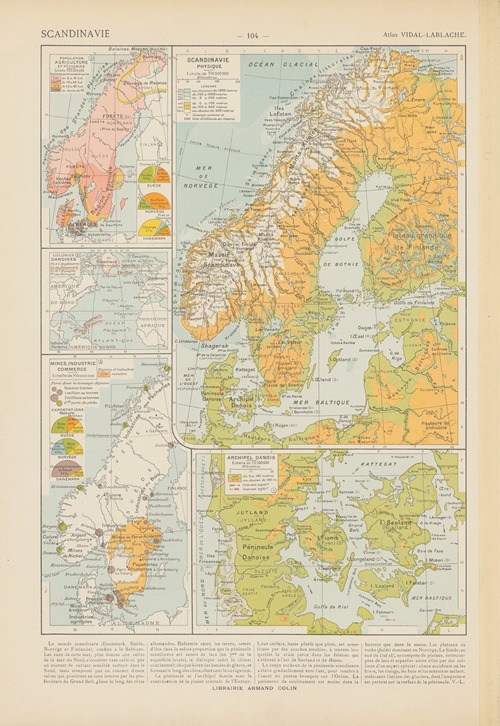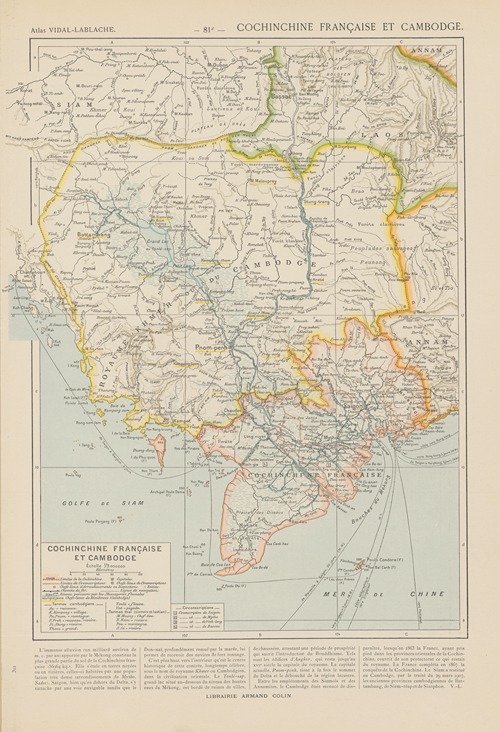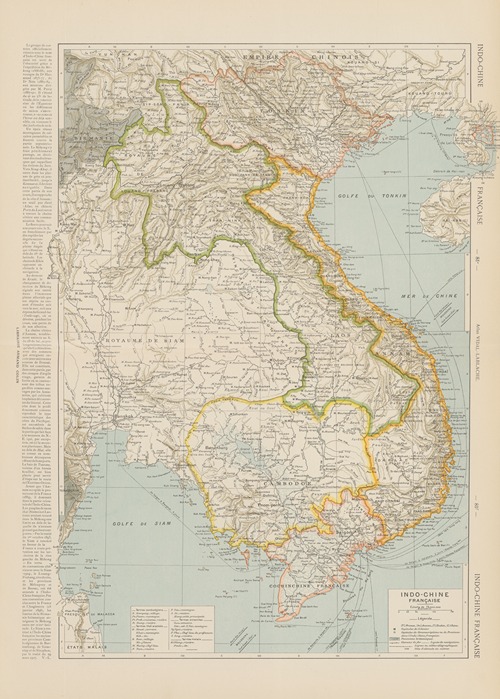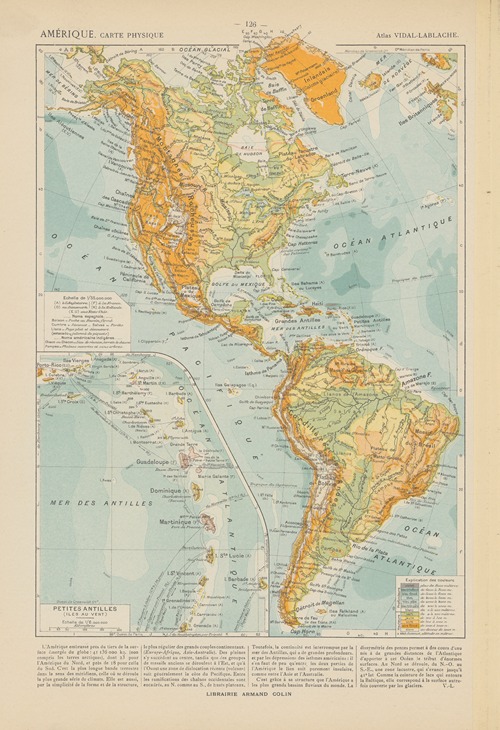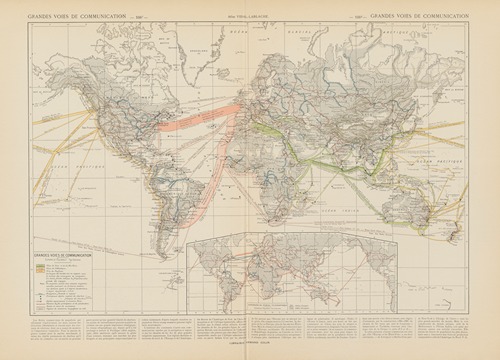

Paul Vidal de La Blache was a French geographer. He is considered to be the founder of modern French geography and also the founder of the French School of Geopolitics. He conceived the idea of genre de vie, which is the belief that the lifestyle of a particular region reflects the economic, social, ideological and psychological identities imprinted on the landscape.
Paul Vidal de la Blache was the son of a teacher at the Collège de Pézenas who subsequently became an academic administrator. He was sent to school at the Institution Favard at the Lycée Charlemagne in Paris. Afterward, he attended the École Normale Supérieure. He entered the École Normale Supérieure in 1863 at the age of eighteen and received the agrégation (certification) in history and geography in 1866. He was appointed to the École française d’Athens, taking advantage of the opportunity to travel in Italy, Palestine, and Egypt (in the latter, being present at the inauguration of the Suez Canal). There he studied Greek archeology for three years.
Upon returning to France, in 1870 he married Laure Marie Elizabeth Mondont, with whom he had five children. He held several teaching positions, notably at the Lycée d'Angers and at the École Préparatoire de l'Enseignment Supérieur des Lettres et des Sciences. La Blache received his doctorate at the Sorbonne in 1872 with a dissertation in ancient history, afterwards published as Hérode Atticus: étude critique sur sa vie. He began working at the Nancy-Université. Vidal de la Blache returned to the École Normale Supérieure in 1877 as a full Professor of Geography and taught there for the next 21 years. He transferred to the Université de Paris, where he continued teaching until he retired in 1909, at the age of 64.
Vidal de la Blache founded the French school of geography and, together with Marcel Dubois and Lucien Gallois, the Annales de Géographie (1893), of which he was the editor until his death. The Annales de Géographie became an influential academic journal that promoted the concept of human geography as the study of man and his relationship to his environment. Vidal de la Blache's pupil Albert Demangeon was deeply influenced by his emphasis on the importance of historical influences in the study of geography, and went on to become France's leading French academic in the field of human geography. During World War I (1914–18) in January 1915 the Geographical Commission was established in close liaison with the 2nd Bureau of the Army Staff with six geographers, Albert Demangeon, Lucien Gallois, Emmanuel de Martonne, Emmanuel de Margerie, Louis Raveneau and Paul Vidal de la Blache. Antoine Vacher contributed intermittently to the work of the Commission.