Edward Lear was an English artist, illustrator, musician, author and poet, now known mostly for his literary nonsense in poetry and prose and especially his limericks, a form he popularised. His principal areas of work as an artist were threefold: as a draughtsman employed to make illustrations of birds and animals; making coloured drawings during his journeys, which he reworked later, sometimes as plates for his travel books; and as a (minor) illustrator of Alfred, Lord Tennyson's poems. As an author, he is known principally for his popular nonsense collections of poems, songs, short stories, botanical drawings, recipes and alphabets. He also composed and published twelve musical settings of Tennyson's poetry.
Lear was born into a middle-class family at Holloway, North London, the penultimate of 21 children (and youngest to survive) of Ann Clark Skerrett and Jeremiah Lear, a stockbroker formerly working for the family sugar refining business. He was raised by his eldest sister, also named Ann, 21 years his senior. Jeremiah Lear ended up defaulting to the London Stock Exchange in the economic upheaval following the Napoleonic Wars; owing to the family's now more limited finances, Lear and his sister were required to leave the family home, Bowmans Lodge, and live together when he was aged four. Ann doted on Edward and continued to act as a mother for him until her death, when he was almost 50 years of age.
Lear suffered from lifelong health afflictions. From the age of six he suffered frequent grand mal epileptic seizures, bronchitis, asthma and, during later life, partial blindness. Lear experienced his first seizure at a fair near Highgate with his father. The event scared and embarrassed him. Lear felt lifelong guilt and shame for his epileptic condition. His adult diaries indicate that he always sensed the onset of a seizure in time to remove himself from public view. When Lear was about seven years old he began to show signs of depression, possibly due to the instability of his childhood. He suffered from periods of severe melancholia which he referred to as "the Morbids".
Lear was already drawing "for bread and cheese" by the time he was aged 16 and soon developed into a serious "ornithological draughtsman" employed by the Zoological Society and then from 1832 to 1836 by the Earl of Derby, who kept a private menagerie at his estate, Knowsley Hall. He was the first major bird artist to draw birds from real live birds, instead of skins. Lear's first publication, published when he was 19 years old, was Illustrations of the Family of Psittacidae, or Parrots in 1830. One of the greatest ornithological artists of his era, he taught Elizabeth Gould whilst also contributing to John Gould's works and was compared by some to the naturalist John James Audubon. After his eyesight deteriorated too much to work with such precision on the fine drawings and etchings of plates used in lithography, he turned to landscape painting and travel.
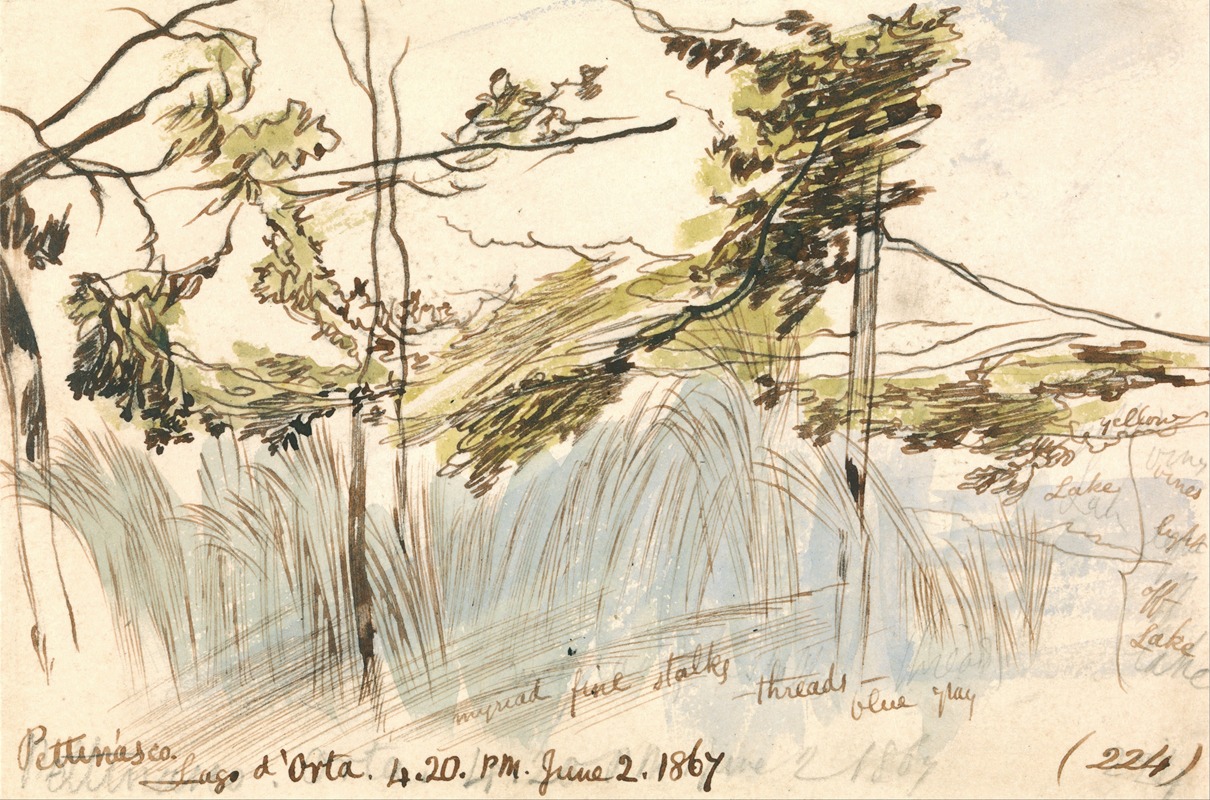
Among other travels, he visited Greece and Egypt during 1848–49, and toured India during 1873–75, including a brief detour to Ceylon. While travelling he produced large quantities of coloured wash drawings in a distinctive style, which he converted later in his studio into oil and watercolour paintings, as well as prints for his books. His landscape style often shows views with strong sunlight, with intense contrasts of colour.
Between 1878 and 1883, Lear spent his summers on Monte Generoso, a mountain on the border between the Swiss canton of Ticino and the Italian region of Lombardy. His oil painting The Plains of Lombardy from Monte Generoso is in the Ashmolean Museum in Oxford.
Throughout his life, he continued to paint seriously. He had a lifelong ambition to illustrate Tennyson's poems; near the end of his life, a volume with a small number of illustrations was published.
In 1842, Lear began a journey into the Italian peninsula, travelling through the Lazio, Rome, Abruzzo, Molise, Apulia, Basilicata, Calabria, and Sicily. In personal notes, together with drawings, Lear gathered his impressions on the Italian way of life, folk traditions, and the beauty of the ancient monuments. Of particular interest to Lear was the Abruzzo, which he visited in 1843, through the Marsica (Celano, Avezzano, Alba Fucens, Trasacco) and the plateau of Cinque Miglia (Castel di Sangro and Alfedena), by an old sheep track of the shepherds.
Lear drew a sketch of the medieval village of Albe with Mount Sirente, and described the medieval village of Celano, with the castle of Piccolomini dominating the vast plain of Lago Fucino, which was drained a few years later to promote agricultural development. At Castel di Sangro, Lear described the winter stillness of the mountains and the beautiful basilica.
Lear primarily played the piano, but he also played the accordion, flute, and small guitar. He composed music for many Romantic and Victorian poems, but was known mostly for his many musical settings of Tennyson's poetry. He published four settings in 1853, five in 1859, and three in 1860. Lear's were the only musical settings that Tennyson approved of. Lear also composed music for many of his nonsense songs, including "The Owl and the Pussy-cat," but only two of the scores have survived, the music for "The Courtship of the Yonghy-Bonghy-Bò" and "The Pelican Chorus". While he never played professionally, he did perform his own nonsense songs and his settings of others' poetry at countless social gatherings, sometimes adding his own lyrics (as with the song "The Nervous Family"), and sometimes replacing serious lyrics with nursery rhymes.
Lear's most fervent and painful friendship was with Franklin Lushington. He met the young barrister in Malta in 1849 and then toured southern Greece with him. Lear developed an infatuation for him that Lushington did not wholly reciprocate. Although they remained friends for almost forty years, until Lear's death, the disparity of their feelings constantly tormented Lear. Indeed, Lear's attempts at male companionship were not always successful; the very intensity of Lear's affections may have doomed these relationships.
The closest he came to marriage was two proposals, both to the same woman 46 years his junior, which were not accepted. For companions, he relied instead on friends and correspondents, and especially, during later life, on his Albanian Souliote chef, Giorgis, a faithful friend and, as Lear complained, a thoroughly unsatisfactory chef. Another trusted companion in San Remo was his cat, Foss, who died in 1887 and was buried with some ceremony in a garden at Villa Tennyson.
Lear travelled widely throughout his life and eventually settled in San Remo, on his beloved Mediterranean coast in the 1870s at a villa he named "Villa Tennyson."
Lear was known to introduce himself with a long pseudonym: "Mr Abebika kratoponoko Prizzikalo Kattefello Ablegorabalus Ableborinto phashyph" or "Chakonoton the Cozovex Dossi Fossi Sini Tomentilla Coronilla Polentilla Battledore & Shuttlecock Derry down Derry Dumps", which he based on Aldiborontiphoskyphorniostikos.
After a long decline in his health, Lear died at his villa in 1888 of heart disease, from which he had suffered since at least 1870. Lear's funeral was described as a sad, lonely affair by the wife of Dr. Hassall, Lear's physician, none of Lear's many lifelong friends being able to attend.
Lear is buried in the Cemetery Foce in San Remo.