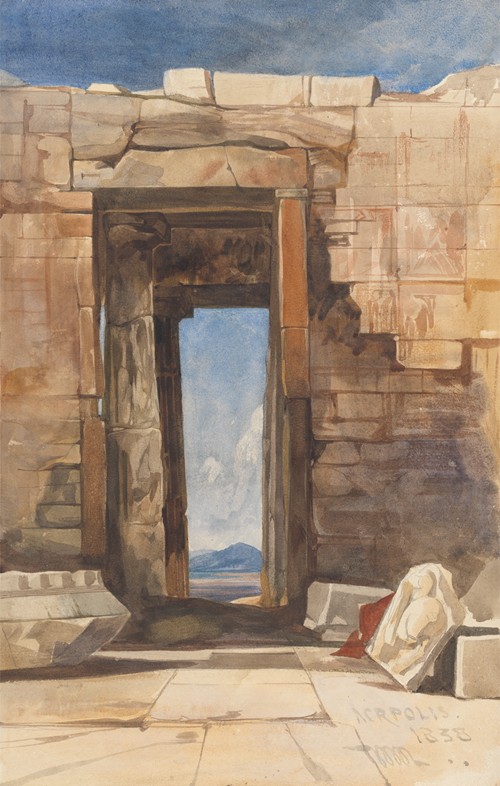
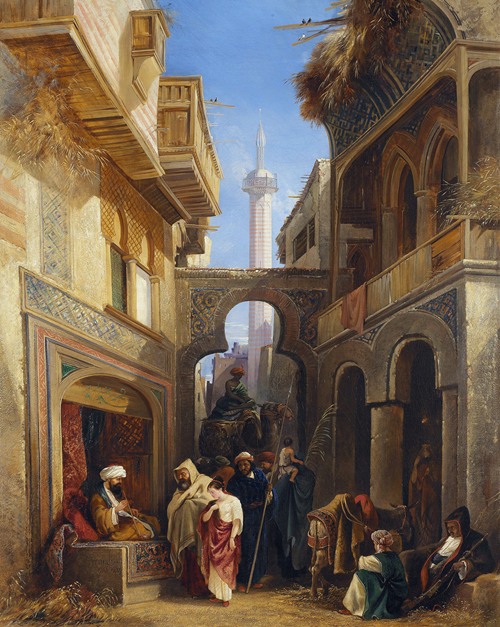
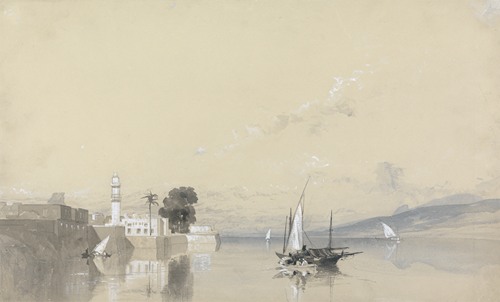William James Müller, also spelt Muller, was a British landscape and figure painter, the best-known artist of the Bristol School.
Müller was born at Bristol, the son of J. S. Müller, a Prussian from Danzig, curator of a museum in Bristol. He first studied painting under James Baker Pyne. His early pictures were mostly of the scenery of Gloucestershire and Wales, and he learned much from his study of Claude, Ruysdael, and earlier landscape-painters. He witnessed the 1831 Bristol riots and recorded some of the scenes in a series of "raw and brilliant oil and watercolour sketches". In 1833 he exhibited at the Royal Academy for the first time, showing Destruction of Old London Bridge-Morning. The next year he made a tour through France, Switzerland and Italy.
He visited the Middle East twice. The first visit was in 1838-39 when he visited Athens, and travelled onwards to Alexandria and Cairo, where he spent two weeks before continuing up the Nile to Luxor, where he made drawings of the ruins and landscapes before returning to Cairo in mid-January. Shortly after his return he left Bristol and settled in London, where he exhibited regularly. His scenes of Egyptian streets and market proved especially popular. His second visit was to Lycia in south west Turkey in 1843-44 when Charles Fellows was removing the Xanthus Marbles for the British Museum. His journey was at the request of the archaeologist Charles Fellows – but at his own expense – Müller and his pupil Harry Johnson accompanied the government expedition to Lycia. He spent three months sketching the landscape and local people around Xanthus, Pinara and Tlos. He spent most of the rest of his life, after his return to England, working on watercolours, and a few oils, of Lycian subjects. The work he carried out at Lycia is considered to be among his finest.
In 1840 he again visited France, where he executed a series of sketches of Renaissance architecture, twenty-five of which were lithographed and published in 1841, in a folio entitled The Age of Francis I. of France.
He died at Bristol on 8 September 1845. Following his death, his work was in great demand; leading to the production of a considerable number of fakes.