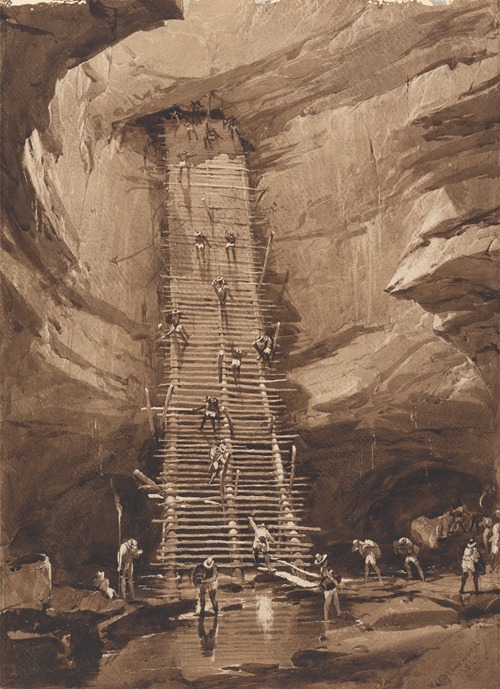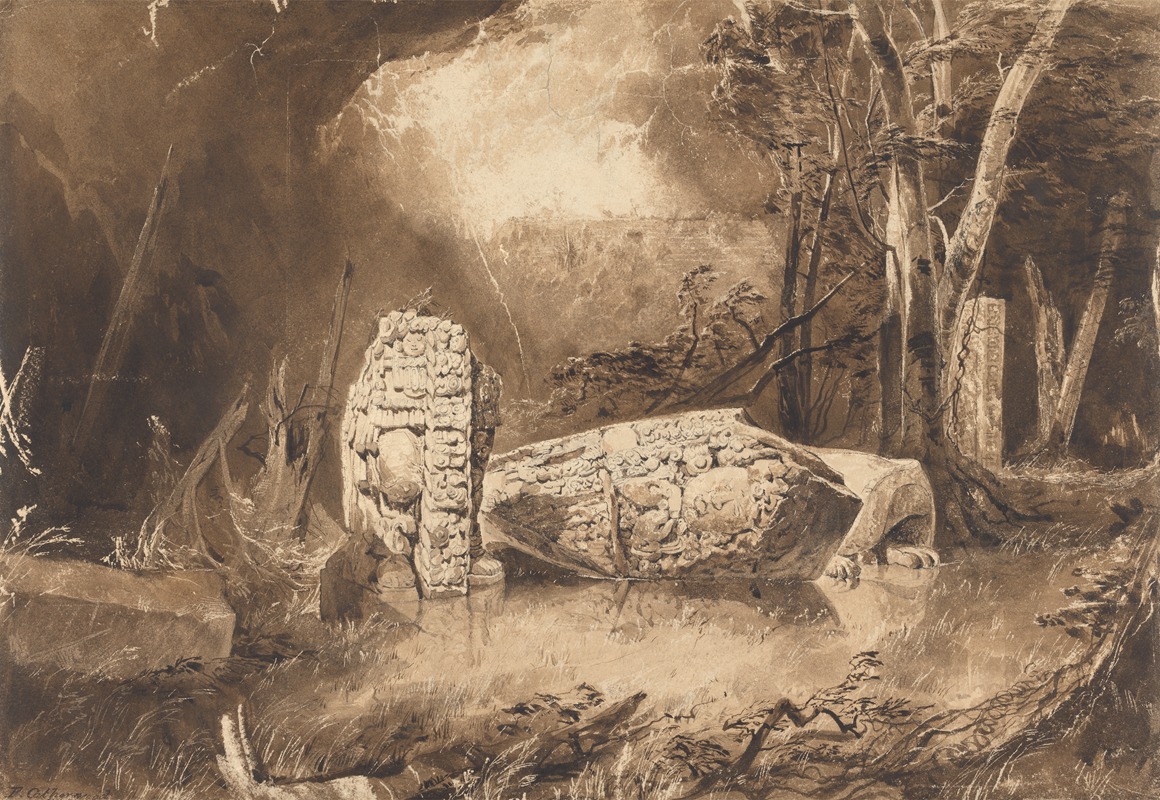
Frederick Catherwood was an English artist, architect and explorer, best remembered for his meticulously detailed drawings of the ruins of the Maya civilization. He explored Mesoamerica in the mid 19th century with writer John Lloyd Stephens. Their books, Incidents of Travel in Central America, Chiapas and Yucatán and Incidents of Travel in Yucatán, were best sellers and introduced to the Western world the civilization of the ancient Maya. In 1837, Catherwood was elected into the National Academy of Design as an Honorary member.
Catherwood, having made many trips to the Mediterranean between 1824 and 1832 to draw the monuments made by the Egyptians, Carthaginians, and Phoenicians, stated that the monuments in the Americas bear no architectural similarity to those in the Old World. Thus, they must have been made by the native people of the area. Catherwood made visits to Greece, Turkey, Egypt, and Palestine and with Joseph Bonomi the Younger made drawings and watercolors of the ancient remains there. During a six-week period in 1833, Catherwood was probably the first Westerner to make a detailed survey of the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem.
Catherwood developed a reputation as a topographical artist. He perfected a drawing technique which used the camera lucida and supplied the drawings for the panoramas of Jerusalem and Thebes shown by Robert Burford in Leicester Square.
In 1836 he met travel writer John Lloyd Stephens in London. They read the account of the ruins of Copán published by Juan Galindo, and decided to try to visit Central America for themselves and produce a more detailed and better illustrated account. The expedition came together in 1839 and continued through the following year, visiting dozens of ruins and resulting in the detailed description of 44 sites, many for the first time. Stephens and Catherwood are credited for the rediscovery of the Maya civilization, and through their publications brought the Maya back into the minds of the Western World.
The expedition resulted in the book Incidents of Travel in Central America, Chiapas, and Yucatan, published in 1841, with text by Stephens and engravings based on the drawings of Catherwood.
Stephens and Catherwood returned to Yucatan to make further explorations, resulting in Incidents of Travel in Yucatan in 1843.
The following year Catherwood published Views of Ancient Monuments in Central America, Chiapas and Yucatan, with 25 colour lithographs from watercolours he made at various ruins. This folio was published in May 1844 simultaneously in London and New York in an edition of 300. Some 282 copies are known to survive, mostly held in private collections or libraries.
A large number of his original drawings and paintings were destroyed when the building where he was exhibiting them in New York City caught fire, but a number survive in museums and private collections, often showing more detail than the published engravings.
With the California Gold Rush Catherwood moved to San Francisco, California to open up a store to supply miners and prospectors, which he considered a more likely way to make money than chasing after the gold himself.
In 1854, Frederick Catherwood was a passenger aboard the steamship Arctic, making a crossing of the Atlantic Ocean from Liverpool to New York. On 27 September in conditions of poor visibility, the Arctic collided with the French steamer Vesta, and sank with much loss of life, including Catherwood. Mysteriously Catherwood's name was left off the official casualty lists for weeks until a concerted effort by his friends and colleagues resulted in a belated inclusion of a single line in the New York Herald Tribune, under the listing of "The Saved and the Lost: Mr Catherwood Also is Missing". He was 55 years old.



