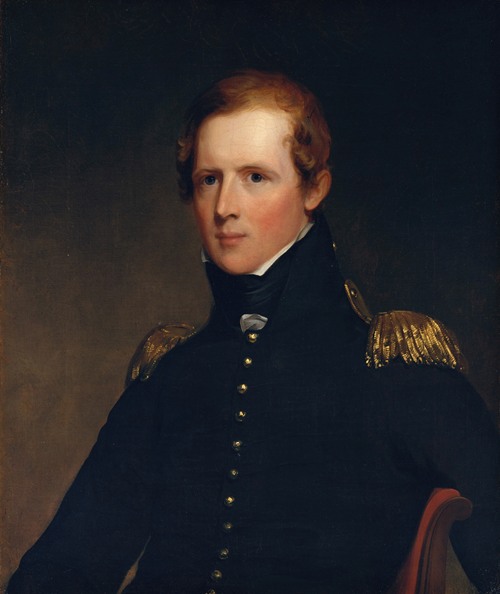
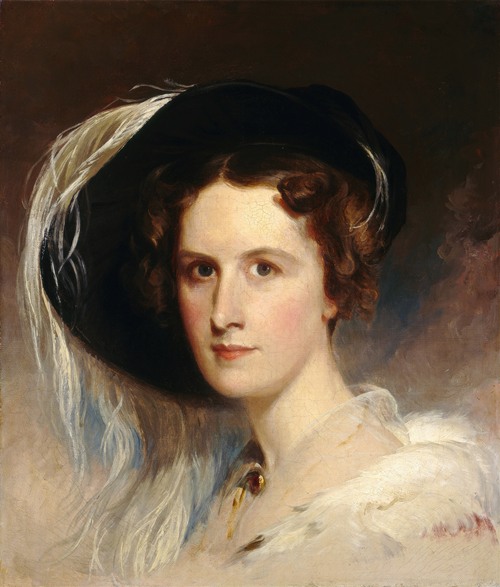
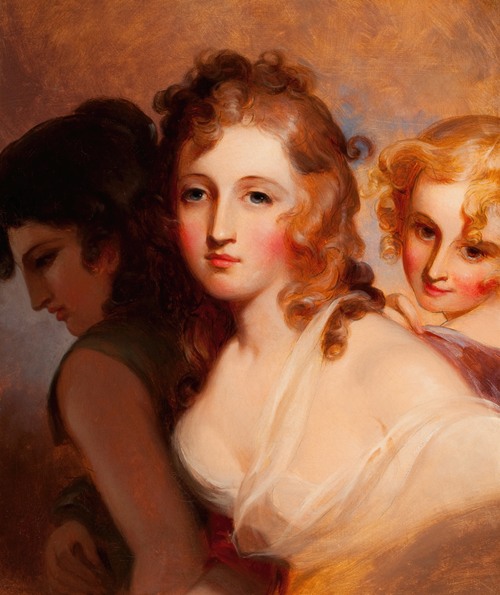
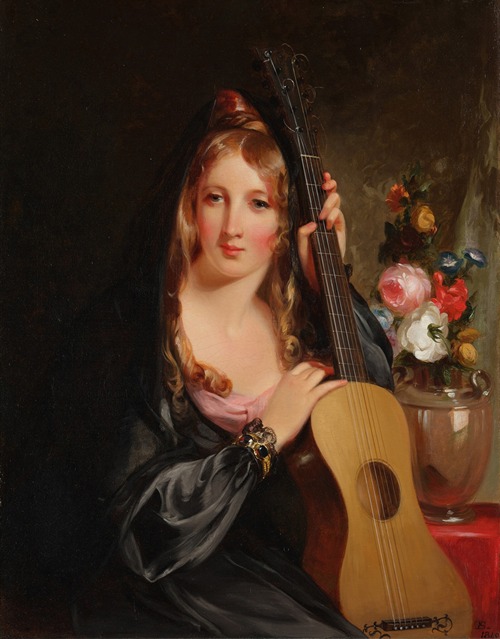
Thomas Sully was an American portrait painter. Born in Great Britain, he lived most of his life in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He painted in the style of Thomas Lawrence. His subjects included national political leaders such as United States presidents: Thomas Jefferson, John Quincy Adams, and Andrew Jackson, Revolutionary War hero General Marquis de Lafayette, and many leading musicians and composers. In addition to portraits of wealthy patrons, he painted landscapes and historical pieces such as the 1819 The Passage of the Delaware. His work was adapted for use on United States coinage.
Sully was born in Horncastle, Lincolnshire, England in 1783 to actors Matthew Sully and Sarah Chester. In March 1792, the Sullys and their nine children emigrated to Charleston, South Carolina, where Thomas's uncle Thomas Wade West managed a theater. Sully made his first appearance in the theater as a tumbler at the age of 11 in Charleston. After a brief apprenticeship to an insurance broker, who recognized his artistic talent, at about age 12 Sully began painting. He studied with his brother-in-law Jean Belzons (active 1794–1812), a French miniaturist, until they had a falling-out in 1799.
He returned to Richmond to learn "miniature and device painting" from his elder brother Lawrence Sully (1769–1804). After Lawrence's death, Thomas Sully married his brother's widow, Sarah (Annis) Sully. He took on the rearing of Lawrence's children. He and Sarah had an additional nine children together. Among the children were Alfred Sully, Mary Chester Sully (who married Sully's protégé, the painter John Neagle), Jane Cooper Sully (who married a Mr. Darley), Blanche Sully, Rosalie Sully, and Thomas Wilcocks Sully.
Sully was one of the founding members of The Musical Fund Society. He painted the portraits of many of the musicians and composers who were also members. In 1835, Sully was elected a member of the American Philosophical Society.
Sully became a professional painter at age 18 in 1801. He studied portrait painting under Gilbert Stuart in Boston for three weeks. After some time in Virginia with his brother Lawrence, Sully moved to New York. He settled in Philadelphia in 1806, where he resided for the remainder of his life. In 1809 Sully traveled to London for nine months of study under the American Benjamin West, who had established his painting career in Great Britain.
Sully's 1824 portraits of John Quincy Adams, who became President within the year, and the general Marquis de Lafayette, appear to have brought him widespread recognition. His Adams portrait is held in the National Gallery of Art, Washington. Many notable Americans of the day had their portraits painted by him. In 1837–1838, he was in London to paint Queen Victoria at the request of Philadelphia's St. George's Society. His daughter Blanche assisted him as the Queen's "stand-in", modeling the Queen's costume when she was not available. One of Sully's portraits of Thomas Jefferson is owned by the Jefferson Literary and Debating Society at the University of Virginia and hangs in that school's rotunda. Another Jefferson portrait, this one head-to-toe, hangs at West Point, as does his portrait of General Alexander Macomb.
Sully's records say that he produced 2,631 paintings from 1801, most of which are currently in the United States. His style resembles that of Thomas Lawrence.(cf. Rilla Evelyn Jackman "AMERICAN ARTS" 1928 pg. 61) Though best known as a portrait painter, Sully also made historical pieces and landscapes. An example of the former is the 1819 The Passage of the Delaware, now in the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston.
Sully died in Philadelphia on November 5, 1872 and was interred in Laurel Hill Cemetery.
His book Hints to Young Painters was published posthumously.
His paintings are held and displayed permanently in many of the world's leading art museums. Two of Sully's portraits hang in the chambers of the Dialectic and Philanthropic societies of the University of North Carolina. Portraits, including that of President James K. Polk, were commissioned of notable alumni from the Societies. The obverse design of the United States Seated Liberty coinage, which began with the Gobrecht dollar in 1836 and lasted until 1891, was based on his work. The Sully painting Portrait of Anna and Harriet Coleman was sold at auction in 2013 for $145,000.
His son, Alfred Sully, served as a brigadier general in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Through Alfred, Thomas Sully is the great-grandfather of Ella Deloria, the noted Yankton Dakota ethnologist and writer; the great-grandfather of artist Mary Sully (also known as Susan Mabel Deloria, 1896–1963); and the great-great-grandfather of Vine Deloria, Jr., Standing Rock Dakota scholar and author of Custer Died For Your Sins (1969), an American Indian civil-rights manifesto.
Sully was a great-uncle of Thomas Sully (1855–1939), the New Orleans-based architect.
Charles Henry Lanneau of South Carolina was his student; he became a portrait painter and Civil War artist.
The World War II Liberty Ship SS Thomas Sully was named in his honor.