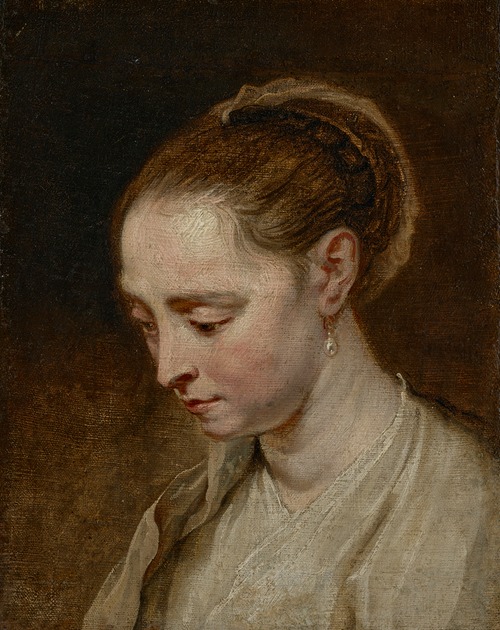
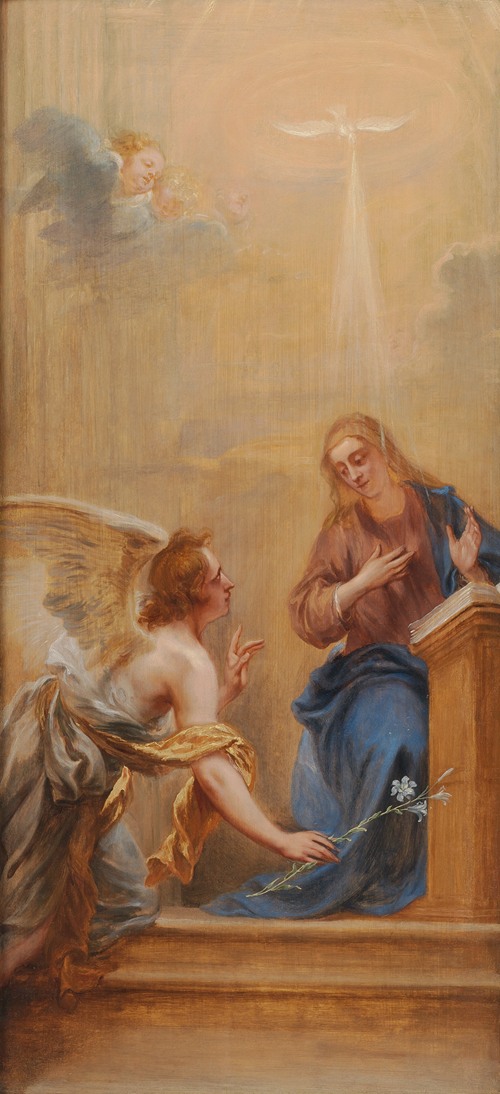
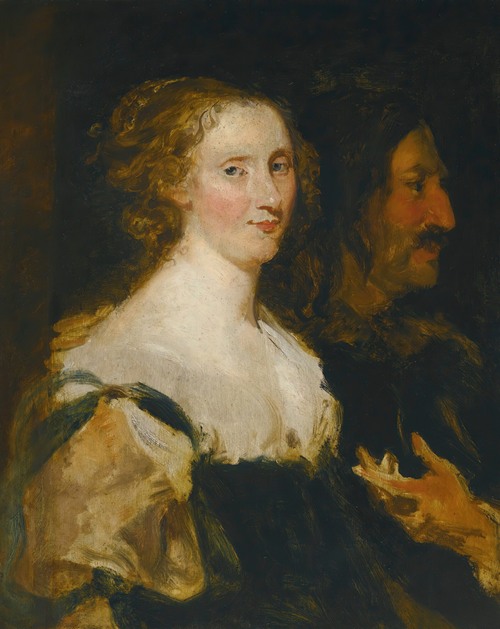
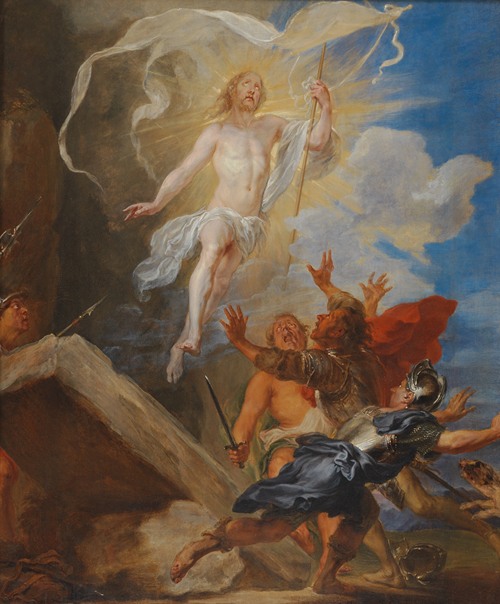
Jan Boeckhorst or Johann Bockhorst, was a German-born Flemish Baroque painter and draughtsman. He was a versatile artist who produced history paintings, genre scenes and portraits in a style influenced by the trio of leading Baroque painters in Antwerp Peter Paul Rubens, Anthony van Dyck and Jacob Jordaens. Boeckhorst also worked as a designer of cartoons for tapestries.
Jan Boeckhorst was born in Münster, Westphalia as the second oldest of twelve children. His family belonged to Münster’s highly respected citizens (Honoratioren) and his father Heinrich was for a while the mayor of Münster. Jan Boeckhorst became a canon in the Jesuit order at age 17. He only started his artistic study when he was about twenty-two years of age.
In the mid 1620s Boeckhorst moved to Antwerp apparently to study with Peter Paul Rubens. There is no firm evidence that Boeckhorst actually studied under Rubens, only a statement by Rubens’ nephew Philip to that effect. However, a close relationship between the artists during the 1630s is documented. Boeckhorst likely also briefly trained with Jordaens during Rubens' stay in London in the late 1620s. In Antwerp, Boeckhorst was known as Lange Jan (Tall John) because of his tall stature.
From 1626 to 1635 Boeckhorst worked on a commission paid for by the devout merchant Lodewijk De Roomer to complete 26 works for a chapel in the Falcon monastery in central Antwerp (or for St. Joseph’s chapel in the Antwerp convent of St. Augustine). These works on which he collaborated with Jan Wildens are now lost. Between 1627 and 1632 he likely worked closely with Anthony van Dyck who was during that period back in Antwerp after a long stay abroad. The two artists collaborated on individual works of art while Boeckhorst also produced copies after van Dyck.
Jan Boeckhorst became a master in the Antwerp Guild of Saint Luke in 1633–1634. He was a regular collaborator with Rubens in the mid 1630s. He first worked on the decorations for the 1635 Joyous Entry (the so-called 'Pompa Introitus') into Antwerp of the new governor of the Habsburg Netherlands Cardinal-Infante Ferdinand. Rubens was in overall charge of this project. For the Pompa Introitus Broeckhorst contributed architectural elements on the 'Arch of Isabella' and the figures of 'Securitas' and 'Salus publica' in collaboration with Gerard Seghers and Jan Borchgraef.
Boeckhorst traveled to Italy in 1635. He returned to Antwerp and in the period 1636–1638 he collaborated with Rubens’ workshop on a large commission to make mythological decorations for the hunting pavilion Torre de la Parada of the Spanish king Philip IV near Madrid. For this project Jan Boeckhorst painted decorations after oil sketches by Rubens.
In 1639 Boeckhorst traveled to Italy again where he resided in Rome. In Rome he likely joined the circle of Dutch and Flemish artists in Rome known as the Bentvueghels. It was the custom among the Bentvueghels to adopt a nickname. Boeckhorst's nickname was possibly Doctor Faustus.
The date of his return to Antwerp is not known with certainty and estimates vary from 1639 to 1649. It is known that he completed a few unfinished works of Rubens' after Rubens' death in 1640. After his return to Antwerp he received multiple commissions from religious institutions in Flanders including for the Saint James Church in Bruges and the Saint Michael's Church and Saint James Church in Ghent.
Jan Boeckhorst died on 21 April 1668 in Antwerp where he was buried in the Saint James Church. His large collection was sold after his death in a sale which lasted six days and raised the considerable sum of 6,026 guilders. His collection included a complete set of early drawings of Rubens.