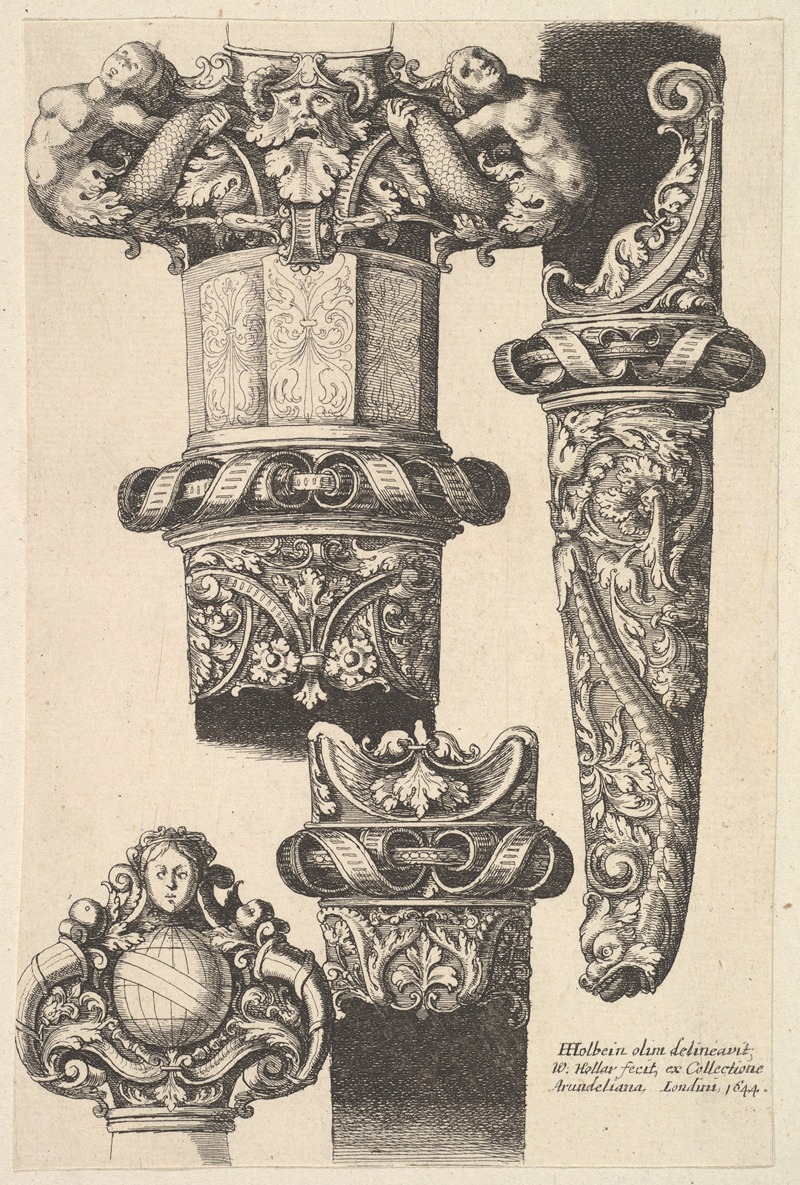
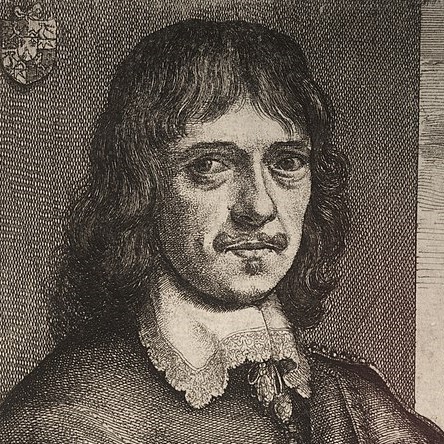
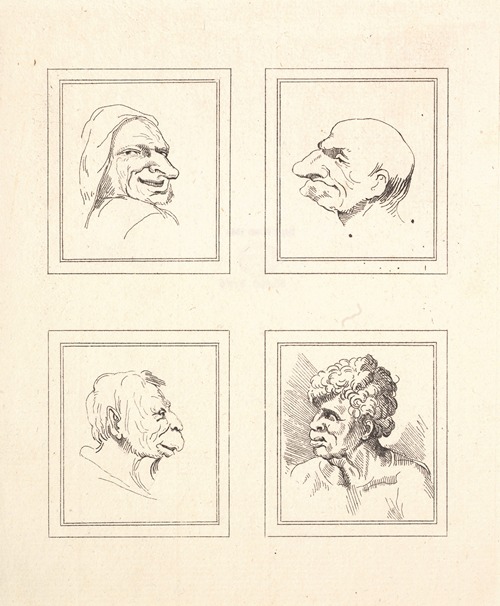
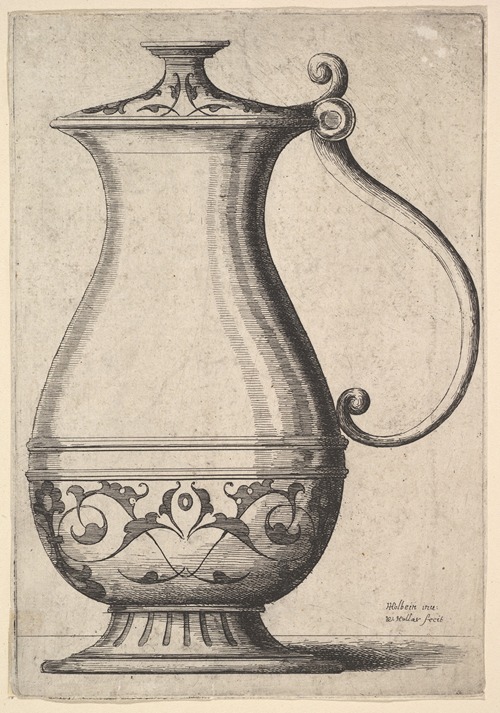
Wenceslaus Hollar was a prolific and accomplished Bohemian graphic artist of the 17th century, who spent much of his life in England. He is known to German speakers as Wenzel Hollar; and to Czech speakers as Václav Hollar Czech: [ˈvaːtslav ˈɦolar]. He is particularly noted for his engravings and etchings. He was born in Prague, died in London, and was buried at St Margaret's Church, Westminster.
After his family was ruined by the Sack of Prague in the Thirty Years' War, the young Hollar, who had been destined for the legal profession, decided to become an artist. The earliest of his works that have come down to us are dated 1625 and 1626; they are small plates, and one of them is a copy of a "Virgin and Child" by Dürer, whose influence upon Hollar's work was always great. In 1627 he was in Frankfurt where he was apprenticed to the renowned engraver Matthäus Merian. In 1630 he lived in Strasbourg, Mainz and Koblenz, where Hollar portrayed the towns, castles, and landscapes of the Middle Rhine Valley. In 1633 he moved to Cologne.
It was in 1636 that he attracted the notice of the famous nobleman and art collector Thomas Howard, 21st Earl of Arundel, then on a diplomatic mission to the imperial court of Emperor Ferdinand II. Employed as a draftsman, he travelled with Arundel to Vienna and Prague. In Cologne in 1635, Hollar published his first book. In 1637 he went with Arundel to England, where he remained in the earl's household for many years.
Though he remained an artist in service of Lord Arundel, he seems not to have worked exclusively for him, and after the earl's death in Padua in 1646, Hollar earned his living by working for various authors and publishers, which was afterwards his primary means of distribution. After Lord Arundel's death in 1646, probably at the request of Hendrik van der Borcht, he etched a commemorative print done after a design by Cornelius Schut in Arundel's honour, dedicated to his widow Aletheia. Arundel is seated in melancholy mode on his tomb in front of an obelisk (perhaps commemorating the obelisk of Domitian which he tried to import from Rome), and surrounded by works of art and their personifications.
In 1745, George Vertue paid homage to their association in the vignette he published on page one of his Description of the Works of the Ingenious Delineator and Engraver Wenceslaus Hollar. It featured a bust of Arundel in front of a pyramid, symbolizing immortality, surrounded by illustrated books and the instruments of Hollar's trade.
During his first year in England he created "View of Greenwich", later issued by Peter Stent, the print-seller. Nearly 3 feet (0.9 m) long, he received thirty shillings for the plate, a small fraction of its present value. Afterwards he fixed the price of his work at fourpence an hour, and measured his time by a sand-glass. On 4 July 1641 Hollar married a lady-in-waiting to the Countess of Norfolk. Her name was Tracy; they had two children. Arundel had left England by 1642, and Hollar passed into the service of the Duke of York, taking with him his young family.
Hollar continued to produce works prolifically throughout the English Civil War, but it adversely affected his income. With other royalist artists, notably Inigo Jones and William Faithorne the engraver, he stood the long and eventful siege of Basing House, and as there were some hundred plates from his hand dated during the years 1643 and 1644 he must have turned his enforced leisure to good purpose. An etching dated 1643 and entitled civilis seditio epitomizes the war with a snake with a head at each end pulling in opposite directions in front of the Giza pyramids and sphinx. Hollar took his setting, presumably symbolizing longer term values, directly from an engraving published in George Sandys' Relation of a Journey begun An. Dom 1610.
Hollar joined the Royalist Regiment and was captured by parliamentary forces in 1645 during the siege of Basing House. After a short time he managed to escape. In Antwerp in 1646, he again met with the Earl of Arundel. During this period of the unrest of the Civil Wars, he worked in Antwerp, where he produced many of his most renowned works, including Dutch cityscapes, seascapes, depictions of nature, his "muffs" and "shells". In 1652 he returned to London, and lived for a time with Faithorne near Temple Bar.
In the following years, many books were published which he illustrated: Ogilby's Virgil and Homer, Stapylton's Juvenal, and Dugdale's Warwickshire, St Paul's and Monasticon (part one). However, his work for the booksellers was poorly paid, and Hollar's commissions declined as the Court no longer purchased his works after the Restoration. During this time he also lost his young son, who was reputed to have artistic ability, to the plague.
After the Great Fire of London he produced some of his famous "Views of London"; and it may have been the success of these plates and other cityscapes such as his 1649 Great View of Prague which induced the king to send him, in 1668, to Tangier, to draw the town and forts. During his return to England a desperate and successful engagement was fought by his ship, the Mary Rose, under Captain John Kempthorne, against seven Algerian men-of-war; a battle which Hollar etched for Ogilby's Africa, published in 1670.
He lived eight years after his return, still producing illustrations for booksellers, and continuing to produce well-regarded works until his death, for example a large plate of Edinburgh dated 1670. He died in extreme poverty, his last recorded words being a request to the bailiffs that they would not carry away the bed on which he was dying. Hollar was laid to rest in a tomb in St Margaret's Church, Westminster.