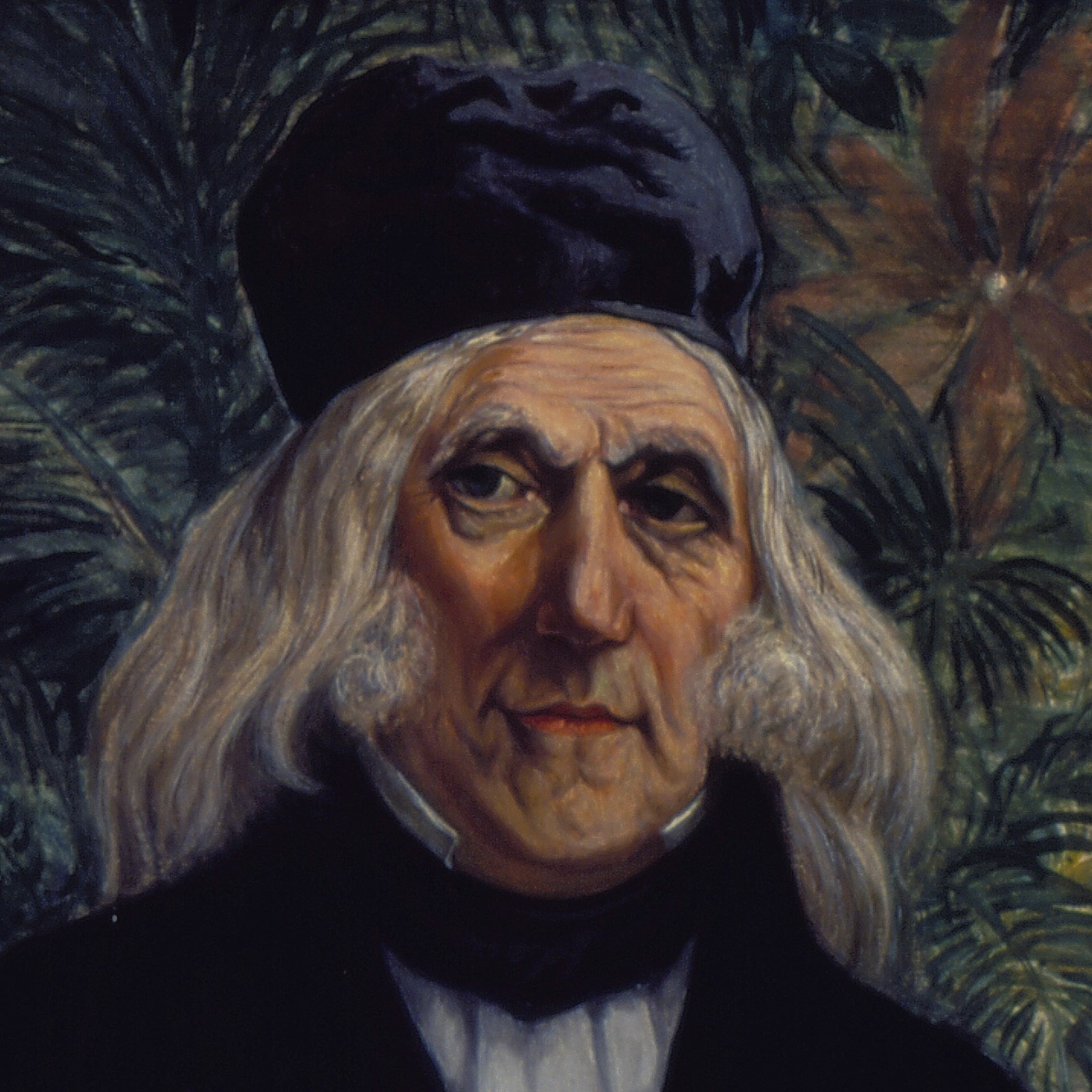
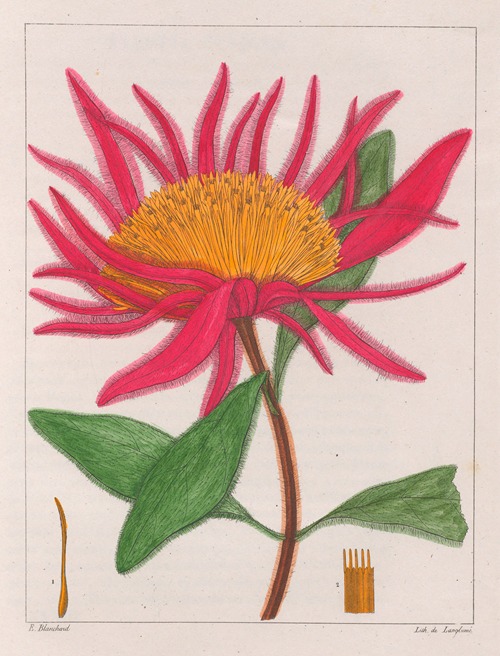
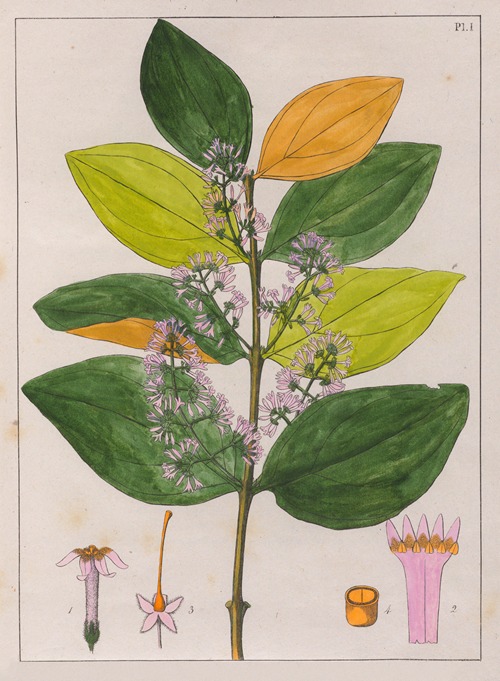
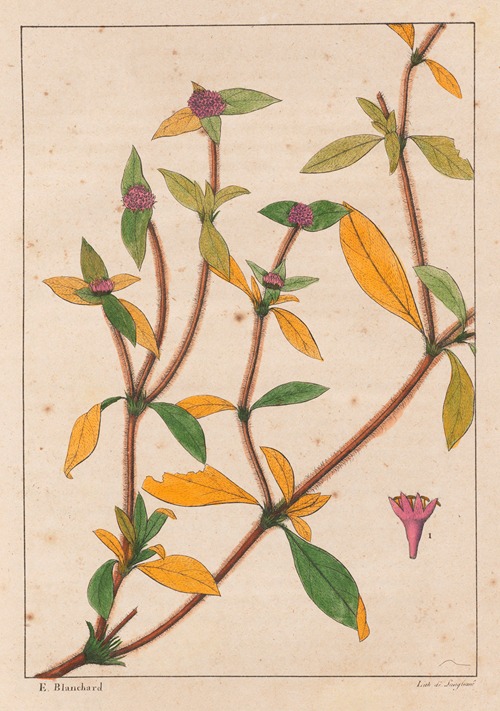
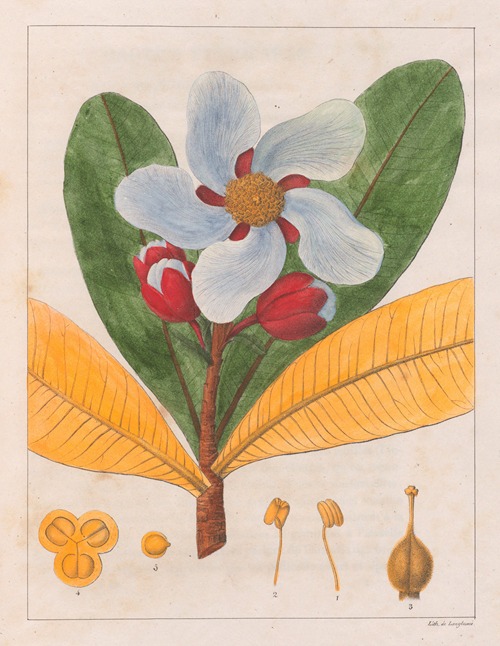
Augustin François César Prouvençal de Saint-Hilaire was a French botanist and traveler who was born and died in Orléans, France .A keen observer, he is credited with important discoveries in botany, notably the direction of the radicle in the embryo sac and the double point of attachment of certain ovules. He also described two families, the Paronychiae and the Tamariscinae, as well as many genera and species.
He began to publish memoirs on botanical subjects at an early age. Between 1816 and 1822 and again in 1830, he traveled in South America, especially in southern and central Brazil, and the results of his study of the rich flora of the regions through which he passed appeared in several books and numerous articles in scientific journals.
In his first voyage, from 1816 to 1822, he explored the Brazilian backlands, traveling ca. 9,000 km, from Southeast Brazil to Río de la Plata , including the former Cisplatina Province (Uruguay). He was able to gather 24,000 specimens of plants, with 6,000 species, 2,000 birds, 16,000 insects and 135 mammals, plus many reptiles, mollusks and fishes. Most of these species were described for the first time. In the next years he devoted himself to the study, classification, description and publication of this huge material, but he was considerably impaired by his ill health, due to diseases contracted during the tropical travels. In 1819 he was appointed correspondent of the Academy of Sciences. He was awarded the Legion of Honor at the level of Chevalier, and the Portuguese Order of Christ.
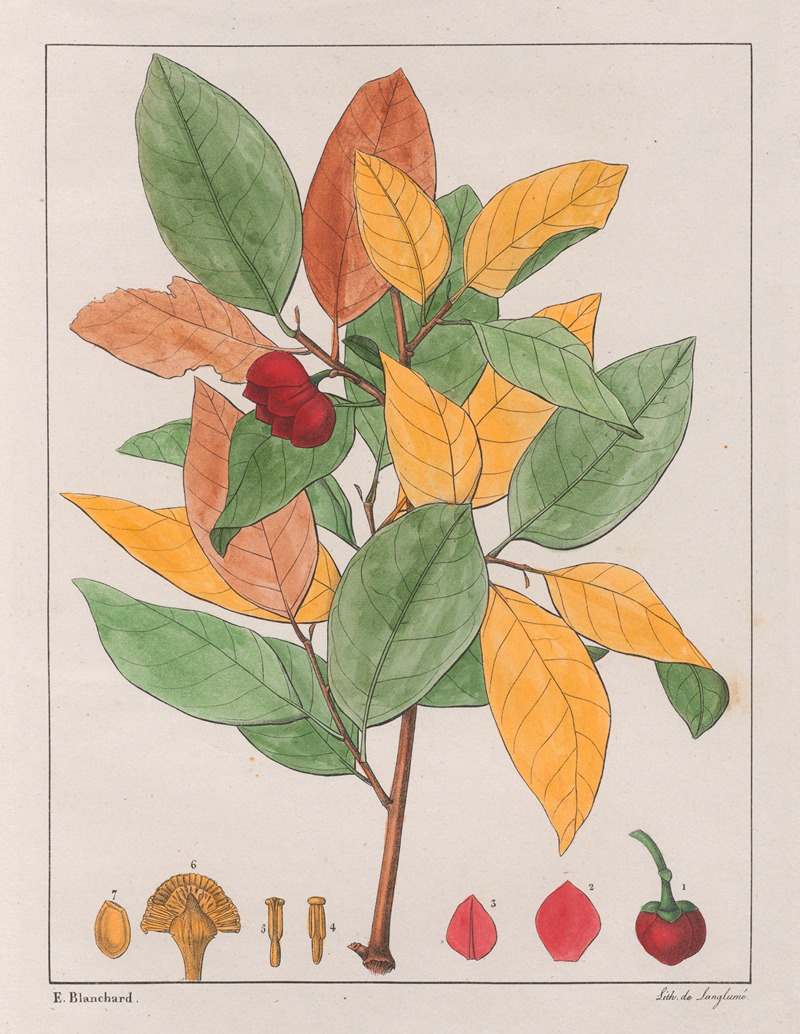
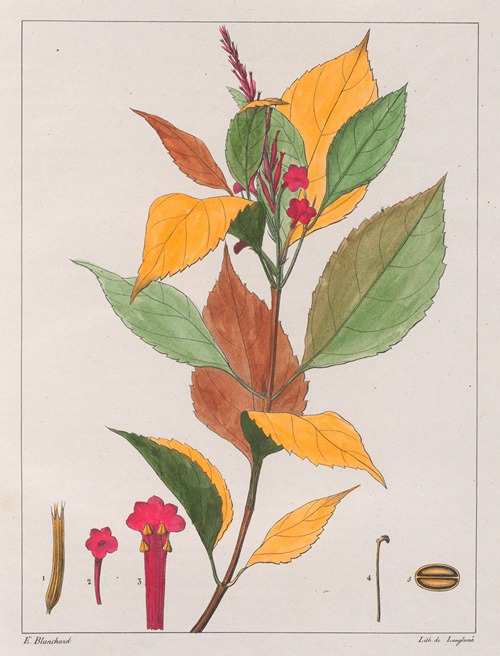
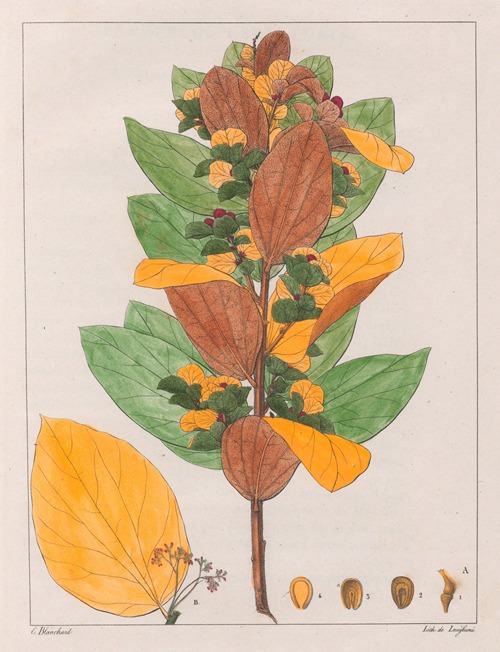
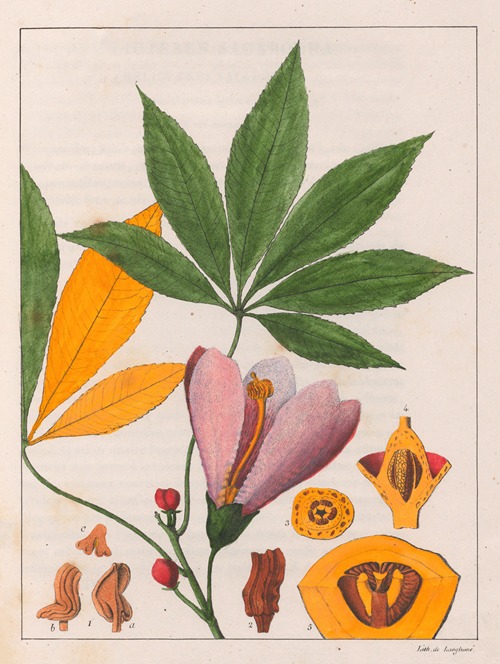
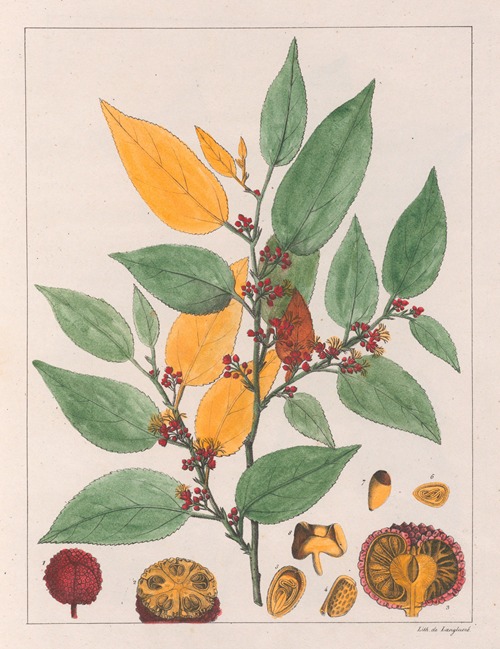
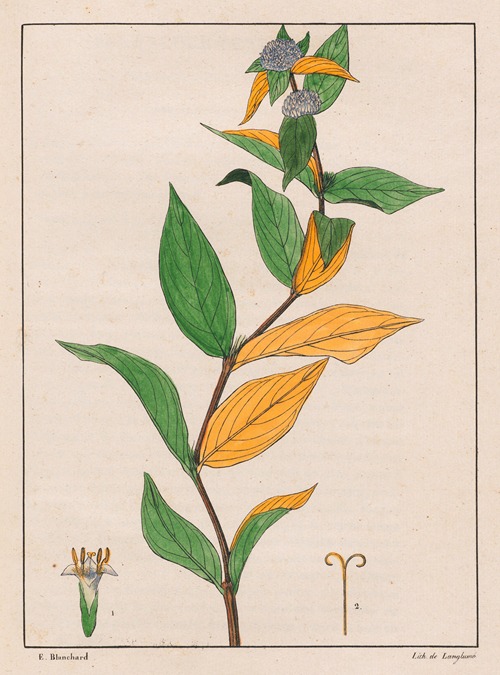
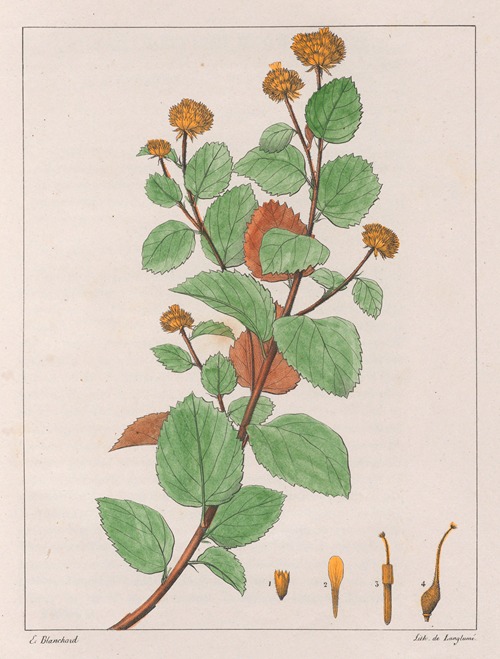
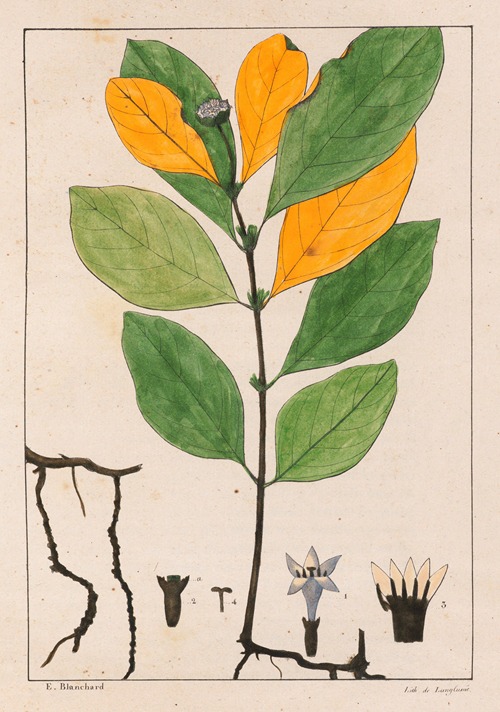
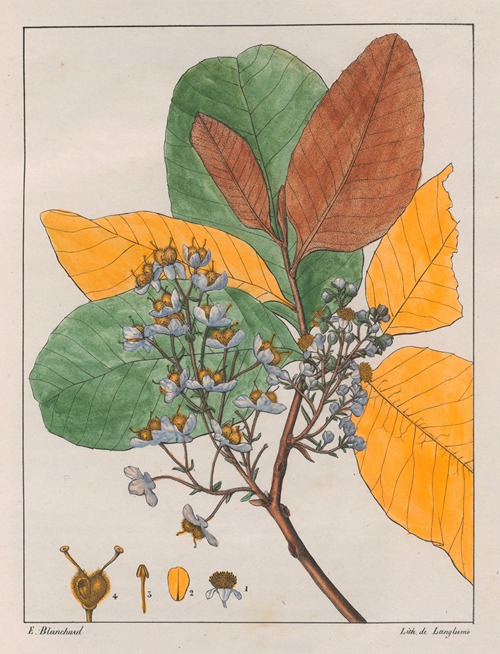
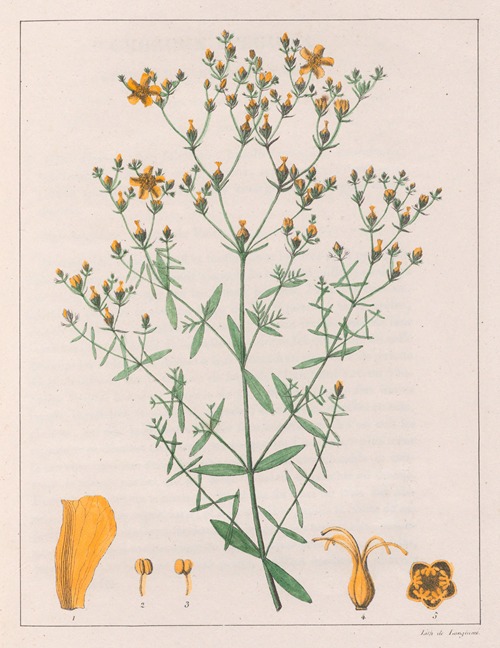
His best-known works are the Flora Brasiliae Meridionalis in three volumes (1825–1832), published in conjunction with Adrien-Henri de Jussieu and Jacques Cambessèdes, and illustrated by Pierre Jean François Turpin; History of the Most Remarkable Plants of Brazil and Paraguay (1824), Usual Plants of the Brazilians (1827–1828), also in conjunction with de Jussieu and Cambessèdes (1828); and Voyage Dans le District des Diamants et sur le littoral du Brésil, in two volumes (1833). His Leçons de Botanique, Comprénant Principalement la Morphologie Végetale (1840), was a comprehensive exposition of botanical morphology and of its application to systematic botany. He died at Orléans on 3 September 1853.