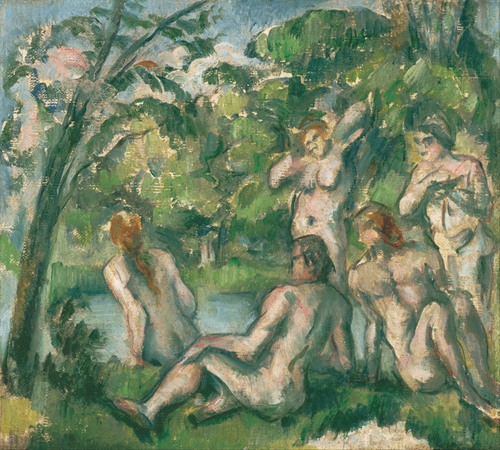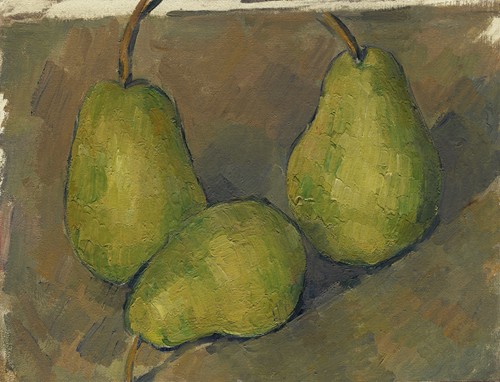Paul Cézanne was a French artist and Post-Impressionist painter whose work laid the foundations of the transition from the 19th-century conception of artistic endeavour to a new and radically different world of art in the 20th century.
Cézanne is said to have formed the bridge between late 19th-century Impressionism and the early 20th century's new line of artistic enquiry, Cubism. Cézanne's often repetitive, exploratory brushstrokes are highly characteristic and clearly recognizable. He used planes of colour and small brushstrokes that build up to form complex fields. The paintings convey Cézanne's intense study of his subjects. Both Matisse and Picasso are said to have remarked that Cézanne "is the father of us all".
The Cézannes came from the commune of Saint-Sauveur (Hautes-Alpes, Occitania). Paul Cézanne was born on 19 January 1839 in Aix-en-Provence. On 22 February, he was baptized in the Église de la Madeleine, with his grandmother and uncle Louis as godparents, and became a devout Catholic later in life. His father, Louis Auguste Cézanne (1798–1886), a native of Saint-Zacharie (Var), was the co-founder of a banking firm (Banque Cézanne et Cabassol) that prospered throughout the artist's life, affording him financial security that was unavailable to most of his contemporaries and eventually resulting in a large inheritance.
His mother, Anne Elisabeth Honorine Aubert (1814–1897), was "vivacious and romantic, but quick to take offence". It was from her that Cézanne got his conception and vision of life. He also had two younger sisters, Marie and Rose, with whom he went to a primary school every day.
At the age of ten Cézanne entered the Saint Joseph school in Aix. In 1852 Cézanne entered the Collège Bourbon in Aix (now Collège Mignet), where he became friends with Émile Zola, who was in a less advanced class, as well as Baptistin Baille—three friends who came to be known as "Les Trois Inséparables" (The Three Inseparables). He stayed there for six years, though in the last two years he was a day scholar. In 1857, he began attending the Free Municipal School of Drawing in Aix, where he studied drawing under Joseph Gibert, a Spanish monk. From 1858 to 1861, complying with his father's wishes, Cézanne attended the law school of the University of Aix, while also receiving drawing lessons.
Going against the objections of his banker father, he committed himself to pursue his artistic development and left Aix for Paris in 1861. He was strongly encouraged to make this decision by Zola, who was already living in the capital at the time. Eventually, his father reconciled with Cézanne and supported his choice of career. Cézanne later received an inheritance of 400,000 francs from his father, which rid him of all financial worries.
In Paris, Cézanne met the Impressionist Camille Pissarro. Initially, the friendship formed in the mid-1860s between Pissarro and Cézanne was that of master and disciple, in which Pissarro exerted a formative influence on the younger artist. Over the course of the following decade, their landscape painting excursions together, in Louveciennes and Pontoise, led to a collaborative working relationship between equals.
Cézanne's early work is often concerned with the figure in the landscape and includes many paintings of groups of large, heavy figures in the landscape, imaginatively painted. Later in his career, he became more interested in working from direct observation and gradually developed a light, airy painting style. Nevertheless, in Cézanne's mature work there is the development of a solidified, almost architectural style of painting. Throughout his life he struggled to develop an authentic observation of the seen world by the most accurate method of representing it in paint that he could find. To this end, he structurally ordered whatever he perceived into simple forms and colour planes. His statement "I want to make of impressionism something solid and lasting like the art in the museums", and his contention that he was recreating Poussin "after nature" underscored his desire to unite observation of nature with the permanence of classical composition.
Cézanne was interested in the simplification of naturally occurring forms to their geometric essentials: he wanted to "treat nature in terms of the cylinder, the sphere and the cone" (a tree trunk may be conceived of as a cylinder, an apple or orange a sphere, for example). Additionally, Cézanne's desire to capture the truth of perception led him to explore binocular vision graphically, rendering slightly different, yet simultaneous visual perceptions of the same phenomena to provide the viewer with an aesthetic experience of depth different from those of earlier ideals of perspective, in particular single-point perspective. His interest in new ways of modelling space and volume derived from the stereoscopy obsession of his era and from reading Hippolyte Taine’s Berkelean theory of spatial perception. Cézanne's innovations have prompted critics to suggest such varied explanations as sick retinas, pure vision, and the influence of the steam railway.
Cézanne's paintings were shown in the first exhibition of the Salon des Refusés in 1863, which displayed works not accepted by the jury of the official Paris Salon. The Salon rejected Cézanne's submissions every year from 1864 to 1869. He continued to submit works to the Salon until 1882. In that year, through the intervention of fellow artist Antoine Guillemet, he exhibited Portrait de M. L. A., probably Portrait of Louis-Auguste Cézanne, The Artist's Father, Reading "L'Événement", 1866 (National Gallery of Art, Washington, D.C.), his first and last successful submission to the Salon.
Before 1895 Cézanne exhibited twice with the Impressionists (at the first Impressionist exhibition in 1874 and the third Impressionist exhibition in 1877). In later years a few individual paintings were shown at various venues, until 1895, when the Parisian dealer, Ambroise Vollard, gave the artist his first solo exhibition. Despite the increasing public recognition and financial success, Cézanne chose to work in increasing artistic isolation, usually painting in the south of France, in his beloved Provence, far from Paris.
He concentrated on a few subjects and was equally proficient in each of these genres: still lifes, portraits, landscapes and studies of bathers. For the last, Cézanne was compelled to design from his imagination, due to a lack of available nude models. Like the landscapes, his portraits were drawn from that which was familiar, so that not only his wife and son but local peasants, children and his art dealer served as subjects. His still lifes are at once decorative in design, painted with thick, flat surfaces, yet with a weight reminiscent of Gustave Courbet. The 'props' for his works are still to be found, as he left them, in his studio (atelier), in the suburbs of modern Aix.
Cézanne's paintings were not well received among the petty bourgeoisie of Aix. In 1903 Henri Rochefort visited the auction of paintings that had been in Zola's possession and published on 9 March 1903 in L'Intransigeant a highly critical article entitled "Love for the Ugly". Rochefort describes how spectators had supposedly experienced laughing fits, when seeing the paintings of "an ultra-impressionist named Cézanne". The public in Aix was outraged, and for many days, copies of L'Intransigeant appeared on Cézanne's door-mat with messages asking him to leave the town "he was dishonouring".
One day, Cézanne was caught in a storm while working in the field. After working for two hours he decided to go home; but on the way he collapsed. He was taken home by a passing driver. His old housekeeper rubbed his arms and legs to restore the circulation; as a result, he regained consciousness. On the following day, he intended to continue working, but later on he fainted; the model with whom he was working called for help; he was put to bed, and he never left it. He died a few days later, on 22 October 1906 of pneumonia at the age of 67, and was buried at the Saint-Pierre Cemetery in his hometown of Aix-en-Provence.