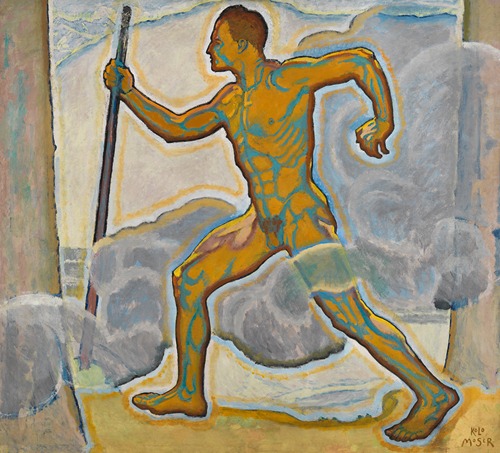
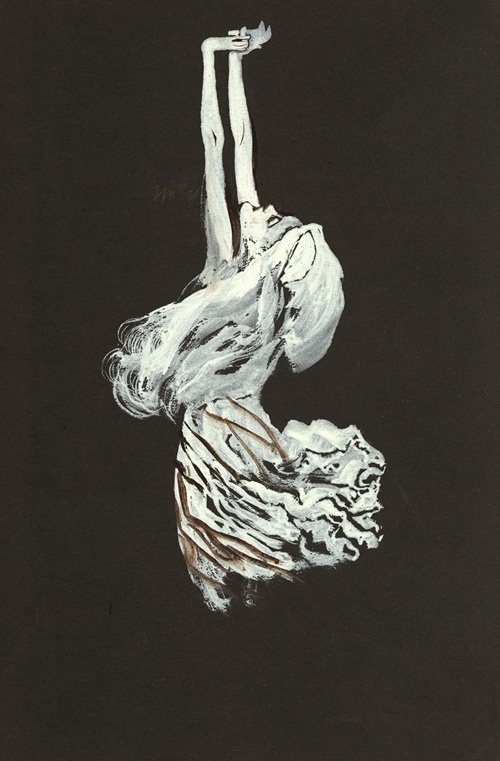
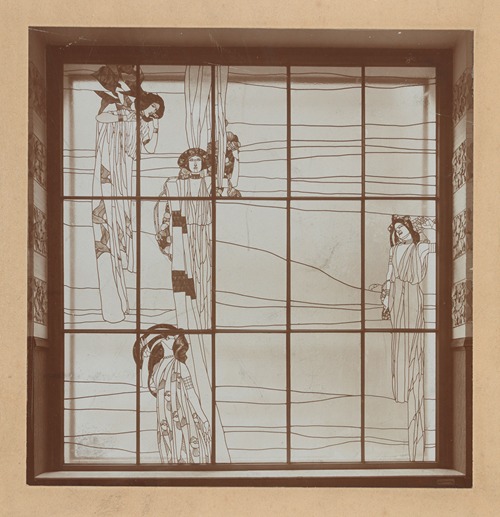
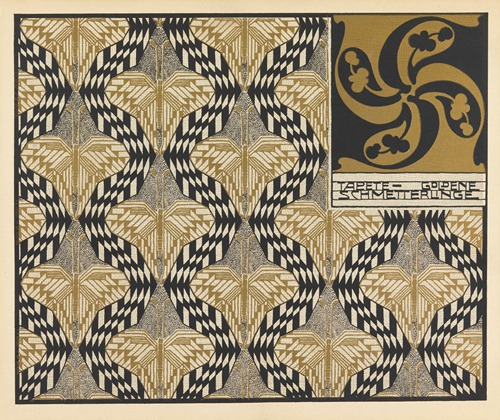
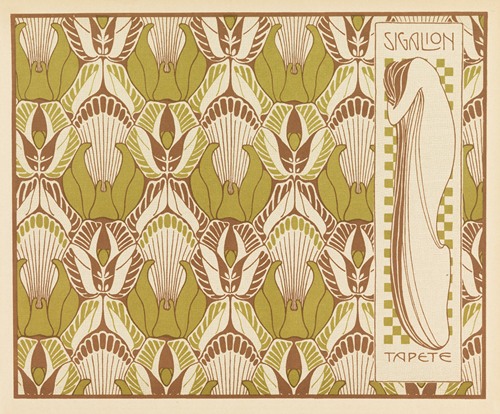
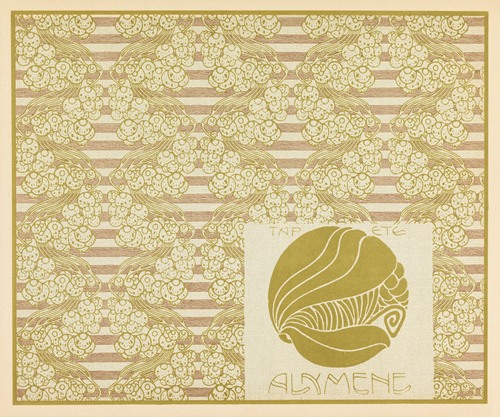
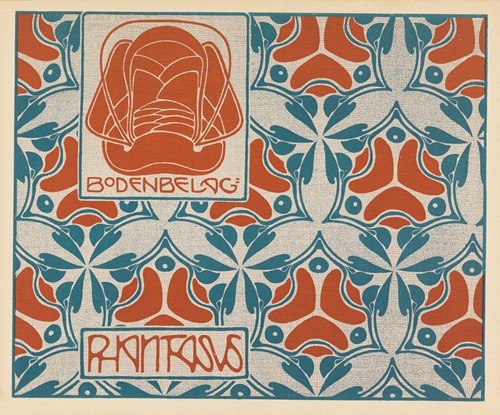
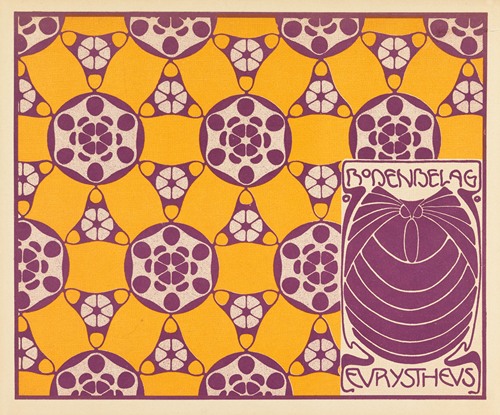
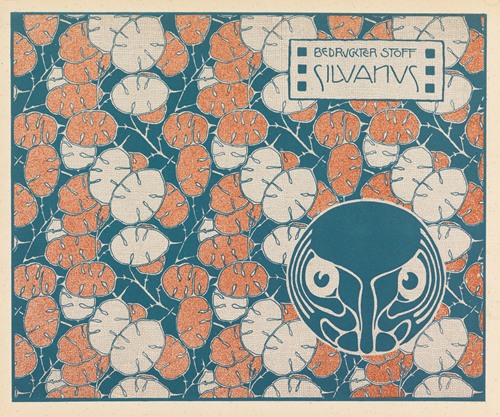

























Koloman Moser was an Austrian artist who exerted considerable influence on twentieth-century graphic art and one of the foremost artists of the Vienna Secession movement and a co-founder of Wiener Werkstätte.
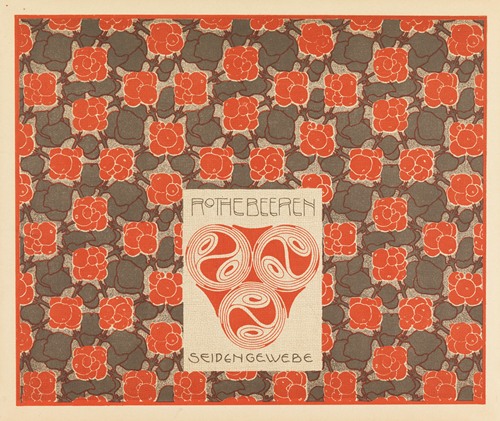
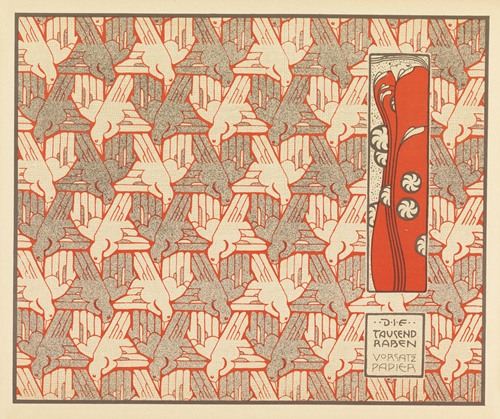
Moser designed a wide array of art works, including books and graphic works from postage stamps to magazine vignettes; fashion; stained glass windows, porcelains and ceramics, blown glass, tableware, silver, jewelry, and furniture.
Born in Vienna, Moser studied at the Wiener Akademie and the Kunstgewerbeschule, where he also taught from 1899.
Moser's designs in architecture, furniture, jewellery, graphics, and tapestries helped characterise the work of this era. He drew upon the clean lines and repetitive motifs of classical Greek and Roman art and architecture in reaction to the Baroque decadence of his turn-of-the-century Viennese surroundings. In 1901/1902, he published a portfolio titled Die Quelle ("The Source") of elegant graphic designs for such things as tapestries, fabrics, and wallpaper.
In 1903, Moser and his colleague Josef Hoffmann founded Wiener Werkstätte, whose studios and artisans produced a number of aesthetically and functionally designed household goods, including glassware, flatware, silverware, rugs and textiles. In 1904, he created the Apse mosaic and glass windows for the Kirche am Steinhof in Vienna, and designed the decoration of the Medallion House of the Linke Wienzeile Buildings for architect Otto Wagner.
In 1905, together with the Klimt group, he separated from the Vienna Secession. The same year, he married Editha (Ditha) Mautner von Markhof, the daughter to one of Austria's great industry fortunes.
In 1907 Moser, due to internal conflicts and as his plans for reorganising the Werkstätte (to cope with financial problems) weren't realised, withdrew from the Wiener Werkstätte.
Moser was one of the designers for Austria's leading art journal Ver Sacrum. This art journal paid great attention to design and was designed mainly by Moser, Gustav Klimt and Josef Hoffmann. His design for the cover of one edition of the art journal was later plagiarized by well known street artist and designer, Shepard Fairey.


























